What is Management: A Complete Guide
Management is the science and art of administration and control of organizations businesses and parastatals. The process of management is not limited to the nature, structure, size, or type of organization or business enterprise.
Management is all-encompassing, including activities such as:
- Setting business and organizational strategies, goals, and objectives
- Coordinating and directing employees and human resources to accomplish set goals and objectives
- Allocating and channeling available financial, technological, and material resources to accomplish objectives.
- And many more.
In this article, I will discuss what is management and other management-related questions to help businesses and organizations.
Table of Contents
What is Management?
In this section, we’ll look at the various ways you can define management. Then, we’ll consider its importance.
What is management? According to Taylor, “Management is an art of knowing what to do when to do it and see that it is done in the best and cheapest way”. Taylor saw management as an indispensable part of every organization. It is an art that smoothens operations at all levels.
Koontz on the other hand defined management as “the art of getting things done through others and with formally organized groups.” (Harold Koontz, 1909 – 1984). Koontz’s definition focused on human management and its importance in accomplishing organizational objectives.
Furthermore, Terry saw management as “a distinct process consisting of planning, organizing, actuating and controlling; utilizing in each both science and art, and followed to accomplish pre-determined objectives.” (George R. Terry, 1877 – 1955). Terry’s definition captures the functional units of management.
Considered the father of management, Drucker envisaged management as a multipurpose organ that manages businesses and managers. He defined management as “the process by means of which the purpose and objectives of a particular human group are determined, clarified and effectuated.” (Peter F. Drucker. 1909 – 2005).
Other relevant definitions include the following:
“Management is defined for conceptual, theoretical and analytical purposes as that process by which managers create, direct, maintain and operate purposive organization through systematic, coordinated co-operative human effort.” (MC Farland).
“Management is what a manager does.” (Louis Allan).
“To manage is to forecast and plan, to organize, to compound, to coordinate and to control.” (Henry Fayol).
“Management is that function of an enterprise which concerns itself with direction and control of the various activities to attain business objectives. Management is essentially an executive function; it deals with the active direction of the human effort.” (William Spriegal)
“Management means decision-making.” (Ross Moore)
“Management is simply the process of decision making and control over the action of human beings for the express purpose of attaining pre-determined goals.” (Stanley Vance)
“Management is the art and science of decision making and leadership.” (Donald J. Clough)
In fact, there are many management definitions as there are scholars who understand the concept of management.
Looking at each definition, we’ll deduce that Management is a universal phenomenon for every individual and organization. It is management that helps and directs an individual’s efforts toward a specific purpose.
Why is management important to an organization?
We can therefore infer the following as the importance and necessity of management to every organization.
- Management helps the organization reach its set targets through strategic planning.
- It helps ensure that organizations utilize their available resources to achieve tangible results within a specified period.
- Through effective management, costs are reduced and profits increased.
- It helps guide, organize and direct human and material resources to ensure that each step is aligned with the overall objective.
So, management is important in every business or organization.
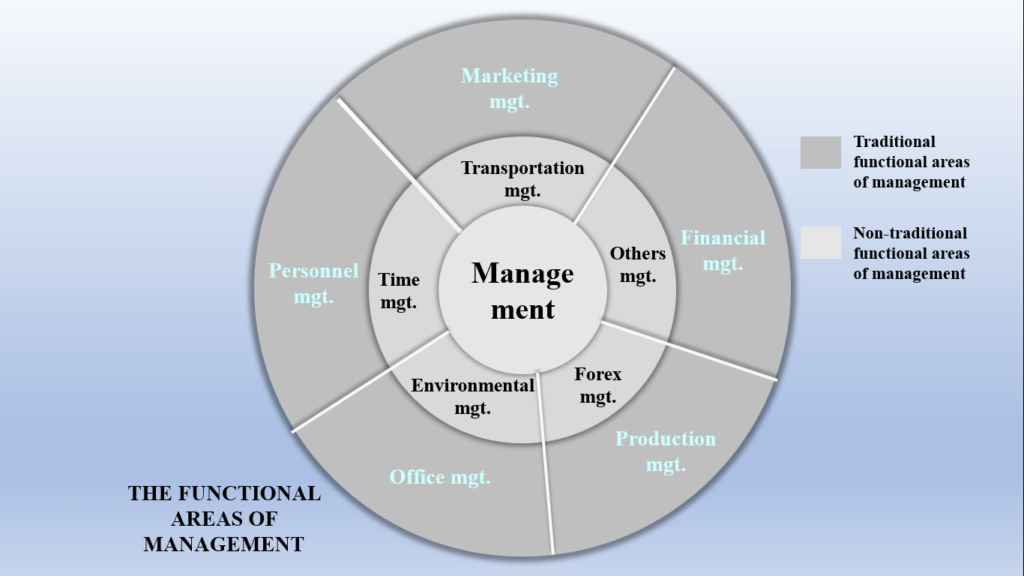
Mention the functional areas of management
The functional areas of management are a group or departmental activities directed toward the success of an organization. There are five functional areas of management, though other non-traditional areas are being added in recent times.

Some of the non-traditional areas that are necessary for today’s management include:
- Time management – which looks at the possibility of accomplishing tasks in the shortest possible time.
- Environmental management – here effort is made to cushion the effect of environmental pollution, especially, from production plants.
- Transportation management – looks at the efficiency of transport and logistic services to minimize overhead costs.
- Forex management – which considers principles that will enable the organization to gain more foreign exchange.
Outside these areas, the traditional areas include marketing management, financial management, personnel management, and office and production management. Let’s look at each of them briefly.
Marketing management
All managerial tasks connected to marketing are referred to as marketing management. Marketing encompasses all of the consumer-related operations, from understanding their needs to ensuring their happiness. Marketing Management is the practice of all managerial tasks in the context of marketing.
Marketing management includes activities such as:
- Making plans for brand awareness and marketing promotions.
- Strategizing and organizing marketing activities.
- Getting qualified personnel needed to carry out marketing tasks.
- Directing and controlling all marketing activities to achieve the overall organizational objective.
Because marketing is the heart of every organization, marketing management is very crucial. Key objectives of marketing management include:
- To effectively manage marketing-related managerial tasks.
- To effectively manage the marketing function.
- To generate the highest possible profits for the organization.
- To increase market share.
- To serve the local and international community.
- To guarantee customer satisfaction.
The marketing manager with his team is tasked with the duties and responsibilities of actualizing the marketing objectives.
Financial management
Financial management can be thought of as the study of the connections between funding and the use of funds. Capital budgeting, cost of capital, portfolio management, dividend policy, and short-term and long-term sources of financing are covered under financial management. The basic three choices in financial management related to:
- Investment policies: They set forth how capital budgets and spending will be handled. All funding requests are ranked, and choices are made regarding whether or not to approve funds for the projects requested.
- Financing strategies: To supply the necessary finances for proposed endeavors with the least amount of risk to the business, a suitable blend of short-term and long-term financing is ensured.
- Decisions about dividends: These decisions have an impact on the amount distributed as extra stock and the amount paid to shareholders.
Human resource or personnel management
The process of managing human resources helps the business give employees, employers, people, and executives the facilities they need.
Personnel management is another name for human resource management. As a result, the manager or staff performed all of the planning, organizing, staffing, directing, managing, and coordinating duties in small or medium-sized organizations. However, if the business is huge, the management would struggle to handle all of the functional areas.
Personnel management covers the hiring, placement, induction, orientation, training, motivation, promotion, wage and salary, performance appraisal, transfer, merit-rating, industrial relations, working conditions, trade unions, safety, and welfare plans for employees. Teamwork among employees and supervisors is something that personnel management aims to foster.
Production/ operations management
Planning, organizing, directing, coordinating, and controlling the production function so that desired goods and services can be produced at the appropriate time, in the appropriate amount, and at the appropriate cost is referred to as production management.
Production is a term that refers to the process of making items, and production management is often referred to as manufacturing management. In the modern world, goods include both physical items and services. The mixture of inputs and outputs used by the business to create its goods and services is known as the product.
Production is made up of the following two words:
Inputs – These comprise a range of components and machinery used to convert raw materials into a variety of outputs.
Outputs: Products and services created via the conversion process are considered outputs.
Competition, the global market, government policies, and so on, have an impact on the production of goods and services.
Some authors consider inventory, material, and purchasing management to be an element of production management. These are some of the tasks involved in production management:
- Product/ operations planning and development,
- Plant and office location, layout, and maintenance,
- Production methods and equipment,
- Management of material purchasing and storage, and
- Effective production and operations control.
Office management
An office is a location where various organizational operations are organized and managed. It is the location from which the staff receives instructions and directions.
Office management is the practice of operating this location in a planned manner. According to the American Institute of Management, office management is “the organization of an office to achieve a specific purpose and to make the best use of the staff by employing the most appropriate machines and equipment, the best possible techniques of work, and by providing the most suitable environment”.
The following tasks are included in office management:
- To set up accounts and protect them,
- To facilitate efficient communication,
- To establish a plan,
- To create coordination across several departments
- To have all necessary office supplies available.
- To make the best use possible of all available resources, including staff services.
What is Planning?
Planning is the process of determining the steps necessary to carry out an objective. Foresight, the fundamental ability for mental time travel, is the foundation of planning.
The core job of management is planning, which is choosing in advance what needs to be done when it needs to be done, how it should be done, and who will do it. It is an intellectual process that establishes an organization’s goals and creates numerous action plans to help the organization reach those goals. It lays out precisely how to achieve a particular objective.
Planning is simply thinking before doing something. It enables us to look into the future and choose in advance how to handle the problems we will face in the future. It requires logical reasoning and sound judgment.
It can also be described as the process of selecting among available options. It is acting after careful thought. It serves as an initial step before the subsequent action. Planning is the outlining of future tasks to be carried out to accomplish set goals.
Without planning, managers are unable to properly organize their teams and resources to achieve their goals. Planning is simply the process managers use to establish goals and take the necessary actions to make sure they are met.
Planning begins with the realization that some action must be taken to shift the situation from its existing or current condition to a desired or alternative future state.
If you fail to plan, you have planned to fail
According to Benjamin Franklin, “If you fail to plan, you plan to fail”. This statement is still true today. The fact is that there is no consistent success in a career or life of business without a consistent plan. Life does not happen by chance; we make things happen through continuous planning.
Most times things don’t turn out the way we plan or want them. This is where planning alternatives come into play. Because planning helps us overcome potential or inherent problems, we have the readiness to cushion such problems as they occur.
Planning also helps us see the future and become proactive when things are not going our way. If we fail to plan, we’ll rather become defensive and reactive when we suddenly meet unexpected conditions. This has led to the failure of many businesses.
Therefore, planning is valuable, else, changes in policies and natural occurrences may cause a shock business may not recover from. Generally, the essence of planning can be seen in its importance to businesses and organizations.
Importance of planning
Because planning is concerned with establishing goals and objectives as well as creating a blueprint to achieve them it is important. Hence, every organization needs it for the following reasons.
- Setting goals and deciding on a course of action, aids managers in improving future performance for the good of the organization.
- Focusing on the future reduces risk and ambiguity.
- It makes activity coordination easier. decreases overlap between tasks and get rid of useless effort as a result.
- It outlines what should be done in the future in advance, giving direction for action.
- Future possibilities and risks are uncovered and identified.
- It lays down guidelines for monitoring. It contrasts actual performance with expected performance and works to make necessary corrections.
The planning process
The planning process entails setting goals and accomplishing them. Let’s briefly enumerate the five-step process of planning.
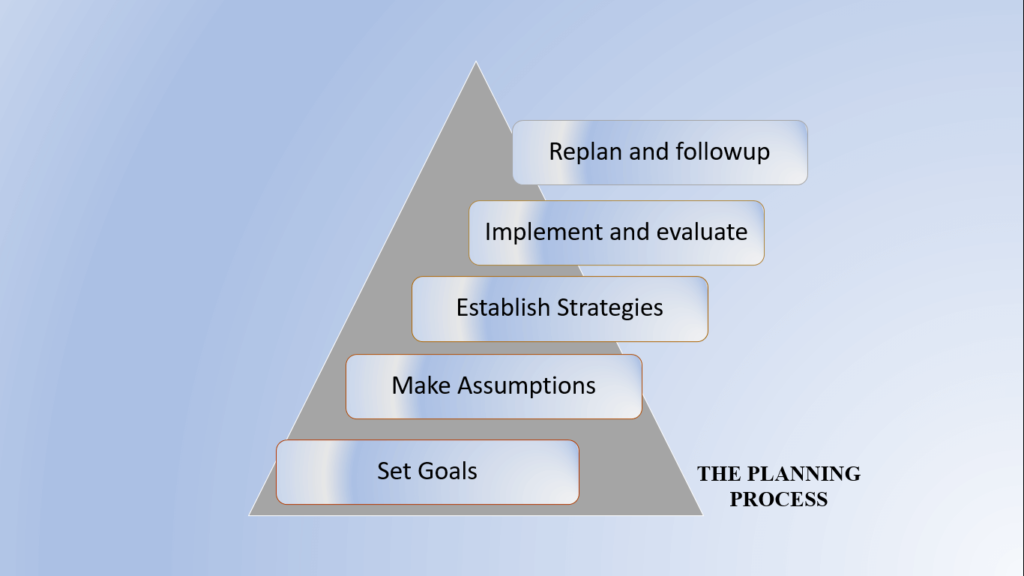
- Setting Goals: The manager of the planning function starts with setting the objectives. This is because all policies, processes, and methods are created just to help achieve the objectives. The managers carefully analyzed the company’s goals, as well as its physical and financial resources, when setting the organization’s objectives. Goals that may be accomplished quickly and within a defined period are frequently established by managers. All personnel is informed of the goals after they have been set.
- Making assumptions and future predictions: Plans are built from the ground up. It is a type of forecast that is made by taking into consideration both the present plans and any prior information regarding different policies. Every premise should be completely agreed upon. Forecasting is used to construct the assumptions. The process of acquiring information is called forecasting. Forecasts are frequently used to assess demand for a product, changes in government or competition policy, the tax rate, and other factors.
- Establishing strategies to accomplish goals: Managers list different approaches to reaching the goals created. He also creates a list of alternatives after determining the organization’s goals. The aim is to ensure that the strategies adopted are suitable for accomplishing the goals.
- Evaluation of a wide range of options: The management starts by making a list of potential options and the underlying presumptions. The manager then starts analyzing each option, noting its advantages and disadvantages. The choice with the highest positive aspect and the most reasonable assumption is selected as the optimal alternative. The viability of each possibility is considered in the evaluation.
- Continual planning necessitates follow-up: Manager’s responsibility does not end with the plan’s execution. Management keeps a careful eye on how the plan is being carried out. It is crucial to monitor a plan since it verifies whether or not the presumptions established about the circumstances and results are still true today. If these forecasts are incorrect, the plan is promptly changed.
What are the attributes of a good plan?
When the definition of planning above is analyzed, we can extract the following attributes of planning.
- Planning is a primary managerial job because it lays the groundwork for other management tasks like organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling, which are all carried out concerning the plans that have been developed.
- It is goal-oriented – It focuses on establishing the organization’s goals, identifying potential courses of action, and selecting the best course of action to pursue to achieve the goals.
- Planning is ubiquitous within the organization – It is pervasive in the sense that it is present in all organizational segments. It is also necessary at all organizational levels. Nevertheless, planning’s scope differs across departments and organizational levels.
- Plans are created using a continuous process for a set period, such as a month, quarter, year, etc. New plans are created after each time frame has passed, taking into account the organization’s existing and future requirements. It is therefore a continuous process because new plans are developed, carried out, and then implemented.
- Planning is an intellectual process – It is a mental workout that requires the use of the intellect to reason, predict, envision creatively, and innovate, among other things.
- Planning is futuristic – We get a glimpse of the future as we make plans. It includes looking forward to analyzing and predicting it so that the organization can deal with upcoming issues successfully.
- Planning enhances decisions making – Choices are made considering the many actions that can be taken to accomplish the aim. The best option should be the one with the fewest negative effects and the greatest number of positive ones.
What is a Goal?
A goal is what you want to achieve in the shortest possible time. It is a kind of milestone covered to arrive at your long-term objective or mission.
A goal is an idea of the future or desired result that a person or organization envisions, plans, and commits to achieve. It represents the decisions we make and the steps we take in order to reach attainment.
Generally, a goal is a fraction of a person’s life or a company’s mission. By this, I mean that it is a part of an overall future or vision you are planning to accomplish. If you reach your targeted goal, you have gone a step towards achieving your life, career, or company’s broad objective.
Goals enable us to achieve focus in life because it helps us to determine what we want. They keep us motivated and propelled, constantly putting us in a state of action. When properly conceived and pursued, it can help us to maximize life.
Goals can be applied to different areas of our lives and they can also be based on a time range. For example, life-based goals can be personal development goals, career goals, educational goals, health goals, etc.
Setting goals is a process of identifying what one wants to achieve in a specified time. That is your ability to articulate and know what you want to accomplish within a given period, say, one year.
What are the steps to achieving a set goal?
To achieve the goals you set for your life, career, or business, you need to take some steps. Among the steps you need to take, these are seven crucial ones.
- Clearly state your desired goal or aspiration. Clarify your goals as precisely as possible. If it is a life goal, your new habit is more likely to succeed if your aim is more specific. If it is a business goal, make it precise.
- Make a list of potential behavioral solutions. Brainstorm the list of actions and steps that you can take to achieve this goal(s). Depending on whether it is a life, career, or business goal, there are numerous action steps to be taken. Consider the steps you think will help you most to achieve the goals you set in step one.
- Ensure that your goals are SMART. SMART is an acronym for a list of standards you might use to establish your goals. It means the following.
Specific – Your goals should be simple, clear, and well-defined. Be sure not to make it too broad. Narrow broad goals down so you can understand exactly what you want to achieve.
Measurable – Your goal should be such that you can measure it. Put in place things that will help you determine the progress of your goal. Ensure that you can be able to calculate how far you have gone in terms of achieving your goal.
Attainable – Your goals must be achievable. Do not set goals that you know you cannot achieve. When setting goals, be sure that your available human, and material resources, put together, will help you achieve your goal.
Relevance – Ensure that your short-term goals relate to what you want in life or a long-term career. If it has nothing to do with your purpose of existence, then it is irrelevant.
Time-bound – You should always set a time limit for when your goal will be achieved. Always specify when your goal will be achieved.
- Put your goals on paper. Writing anything down on paper aids with memory retention and improves comprehension. Instead of typing goals, you should write them out to increase your incentive to achieve them. Be mindful of your wording when writing. Your confidence can be increased by setting goals that state that you “will” attain them rather than “might.” Put your goals down on notepads or index cards and post them in areas where you’ll see them often.
- Draw a plan of action and take steps to carry them out. Create a clear plan to achieve your goals once you have identified them. Start with easy measures like things you can do right now to further your cause. Plans can change depending on the goal and requirements to achieve them. Decide on what you can read or watch about the subject, and how you can practice and apply what you learned.
- Evaluate progress and ensure that you are on track. To manage your time and keep yourself motivated while working toward goals, it’s critical to track your progress. You might want to keep going back and reviewing the initial goal you set and its time range. Due to unforeseen circumstances, some things, like schooling, can take longer than anticipated. Look for opportunities to finish other activities in less time to stay on schedule. You can always refine your plan when things are not working as you’ve planned.
- Be persistent and never look back. The most crucial trait that might assist you in achieving your goal is persistence. It’s crucial to realize that certain steps toward obtaining a goal may be unanticipated. Setting goals is a great way to establish a purpose for your career development. There are some things beyond your control, but making little, consistent progress toward your goal will keep you motivated. If you encounter setbacks, go back and see if any modifications to your plans are necessary.
What is Objective?
Objective is the expectation or expected result to be achieved by an individual, business, or organization within a definite period. It establishes the parameters and guides the concerned work. The organization’s goals are stated regarding the future.
It is the first step in the planning process, which is determined by the company’s top management. It is dependent upon all the other planning elements, such as policy, process, schedule, budget, etc. Objectives address the “why” side of planning.
The organization’s objectives are taken directly from its vision and mission statement. It can be short-term or long-term objectives. For instance, in a business setting maximizing sales and increasing margins are considered short-term objectives. However, the growth and expansion of the business is a long-term objective.
Objectives outline the desired future state of affairs for the organization and serve as a roadmap for all business planning. Each organizational level, division, and unit may have its objective. It takes the form of a written declaration of the objectives that can be achieved in a specific amount of time.
What is the relationship between the plan and objectives?
The relationship between objectives and plans is derived from their meaning. Objective refers to what should be achieved, that is, the result of a thing. The plan is the steps to be taken to achieve the result. Specifically, the following are the relationships between objectives and plans.
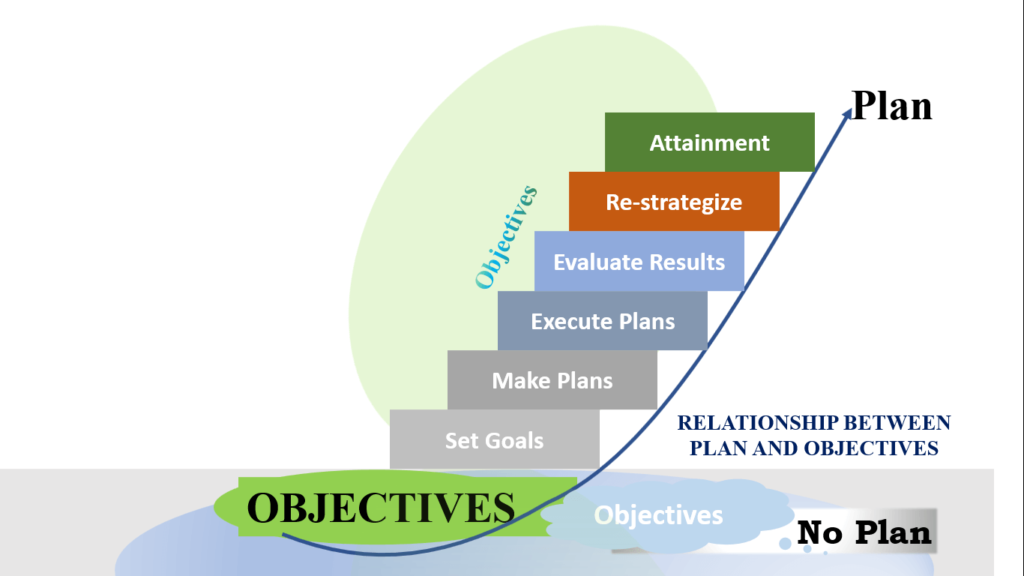
- You can have many objectives, but without a plan on how to achieve them, they’ll never happen. So, plans and objectives are connected such that one does not happen without the other.
- Plans are made based on specified objectives. Without objectives, plans will have no anchor to be based on. For example, you do exercise to lose weight or keep fit. Something (objective) always triggers a plan.
- Objective is the result while plan is the process to actualize the result. This sees objective as the destination while plan is the route to get to the destination.
- Objectives without a plan is a mere wishes. Many people have wished to attain certain heights in life or achieve a definite result. But because there are no efforts put in place to actualize their dream such thoughts remain a wish.
- Objectives are static while plans are dynamic. Except if objectives are vague and need reconstruction, they remain static until they are achieved. However, plans need active effort. This could be the acquisition of knowledge, skills, etc., that will help you attain the objective.
Generally speaking, both objectives and plans are interwoven such that one cannot stand without the other. It is therefore important that we utilize both to achieve success in every area of our lives and business.
If you wake up one day and start heading to nowhere, you will get to nowhere
This statement simply tells us that life does not happen by chance. There is a cause and effect in life. A man without a purpose will always ride on other people’s shoulders. This means that people will detect the course of his life.
Generally speaking, some of the consequences of not planning include:
- Undervaluing yourself and your abilities. Since anything goes, people will not take you serious, and your worth will be determined by anyone and everyone.
- You will lose total control of your life, career, or business.
- You will also have no zeal to learn or grow because you have lost confidence.
- Finally, you will become a burden to society.
Therefore, anyone who wakes up and starts heading nowhere will get to nowhere.
What do you Understand by Management by Objective (MBO)?
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a tactical method for raising an organization’s performance. It is a procedure wherein the management of a company clarifies and communicates to its members its goals with the idea of achieving each target.
It is the process of setting precise organizational goals that management can communicate to team members, then determining how to accomplish each goal one at a time. In MBO, individual goals and organizational goals are aligned.
The goal of MBO is to increase organizational performance by establishing goals that both management and people can support. According to the principle, giving employees a voice in goal development and action planning promotes employee engagement and participation while also coordinating organizational goals.
Peter Drucker originally popularized management by objectives (MBO), also known as management by planning (MBP), in 1954.
The system is a process in which the superior and subordinate mutually identify common goals. Then each individual’s key areas of responsibility in terms of the results expected of him or her are defined. These areas are utilized as measurements and guidelines.
MBO is a comprehensive organizational approach. It involves people from the top to the bottom of the value chain. In MBO, first, the company’s major goals are identified by the managers. They then devise tactics for communicating these goals to employees.
For success to be achieved, this management strategy is based solely on the principle of clarity. Employees are more efficient at accomplishing goals when they are clear about them. The objectives may be challenging but are also achievable.
To guarantee that the plans are effective, all objectives are quantified and monitored. Finally, employees are given feedback depending on their performance. Organizations fine-tune these goals over time, increasing total productivity.
The MBO Process
According to Peter Drucker in his popular book, The Practice of Management, MBO involves 5 steps. Let’s examine them.
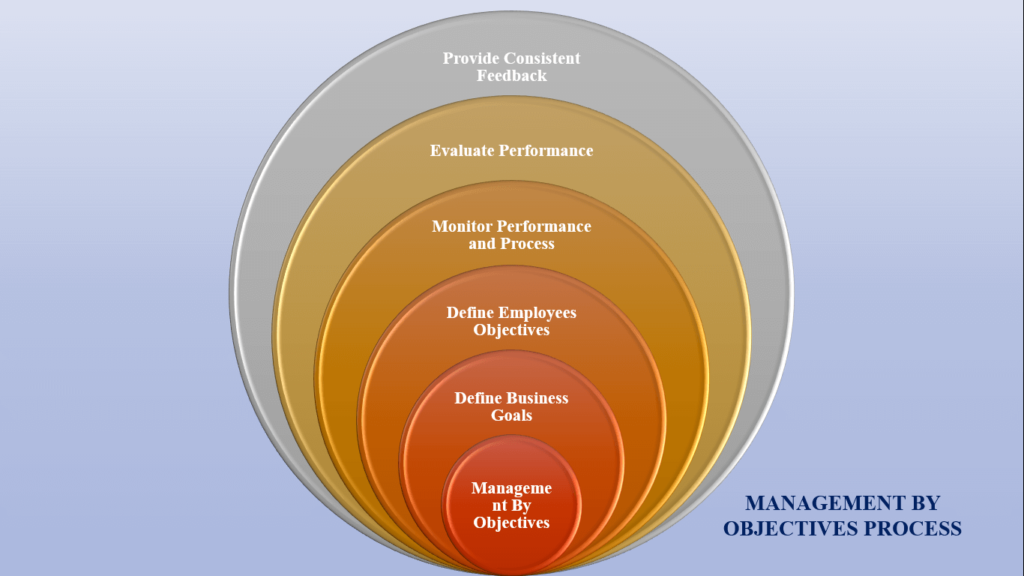
Define organizational goals
The top management set or alters the organization’s present goals. These objectives are taken from the company’s mission. Except for startups, this is usually already specified.
Define the specific objectives of employees
This is the most crucial phase in the management by objectives method. As soon as goals are established, the organization must choose how to achieve them. The objectives will be listed in such a way that employees will have different goals depending on their roles.
It is recommended that each person set one to three goals. Anything more would cause confusion and a lack of focus. The employees’ specific goals are expected to be SMART. This will prevent failures due to unrealistic expectations. Employees should also define their own goals. This will make them feel belonging to the organization and keep them motivated.
Continuous performance and process monitoring
The process should be watched at all times because the outcomes will impact plans. It also keeps management from losing sight of progress. Organizations can avoid failures by identifying weaknesses in the process early on.
This process is vital for boosting managers’ effectiveness and for measuring the performance and advancement of each person in the organization.
Performance evaluation
It is critical to utilize reliable measures to assess performance. Organizations should focus on critical performance metrics from the start.
Organizations should establish boundaries for what is acceptable, successful, and potentially disastrous. Failures should be addressed, and successes should be celebrated.
Providing consistent feedback
Every employee must receive a clear response to their performance. They should be rewarded if they perform well. This encourages them to continue their wonderful work.
Employees who did not meet their objectives, on the other hand, must identify the weaknesses in their approach. They must devise a strategy to overcome the problems and improve.
Advantages of Management by Objectives
- Generally, management by objectives boosts an organization’s productivity over time by continuously evolving the process.
- It improves the management’s teamwork and communication because they must continually collaborate to maintain strategy clarity and provide feedback.
- Employees may be able to reach their objectives more readily since they will be consistent and attainable.
- Key Result Areas (KRAs) are established for each employee based on their interests, educational qualifications, and specialism.
- It improves the organization’s openness and managerial efficiency. As a result, it boosts productivity by reducing uncertainty.
Disadvantages of Management by Objectives
- Because MBO is focused on goals and targets, it frequently overlooks other aspects of an organization. Areas such as conduct culture, a healthy work ethos, and opportunities for involvement and contribution are neglected.
- Employees are under additional pressure to accomplish targets within a given time window.
- Employees are urged to fulfill targets by any means necessary, which means that shortcuts may be utilized and job quality may suffer as a result.
- If management relies only on MBO for all management obligations, it can be difficult in areas where MBO does not apply.
What is Management by Exception (MBE)?
Management by exception (MBE) is a corporate management approach that focuses on recognizing and handling incidents that differ from the norm, as advocated by the project management method as best practice.
It is a strategic approach that states that instead of examining and dealing with each routine business activity, managers and supervisors should examine, investigate, and develop solutions for only those issues where there is a deviation from set standards, norms, business practices, or any other financial goals such as profit deviation, quality issues, infrastructure issues, and so on.
In MBE, only significant deviations from, say, a budget or plan are brought to the attention of management. The aim is that management’s attention will be focused solely on areas that require action. When managers are notified of a deviation, they may focus on one specific issue while staff handles everything else. If nothing is mentioned, management can presume that everything is going as planned.
Management by exception has two applications: general business and business intelligence. General business exceptions are circumstances in which the normal behavior of a business process deviates and requires special treatment, often by human intervention. Process variation, infrastructure or connectivity challenges, external deviation, poor quality business rules, incorrect data, and other factors could be responsible.
Management by exception is the technique of examining, addressing, and dealing with such situations through the use of competent personnel and software tools. The goal of the management by-exception approach is to only worry management with the most significant deviations from the business’s anticipated direction or performance.
Managers will undoubtedly devote more time to addressing and rectifying these deviations. The notion can be fine-tuned so that minor deviations are brought to the notice of lower-level managers, while major deviations are reported directly to high management.
Key stages of MBE
Management by Exception has 6 application stages discussed below.
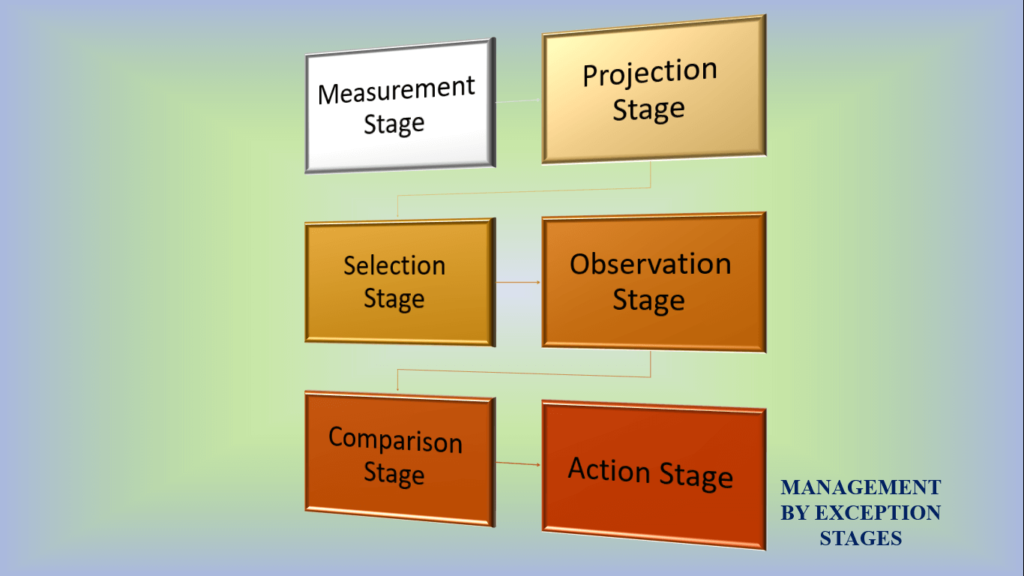
Measurement stage
This first step of management by exception collects and evaluates data on business operations, which includes measuring the performance of all available inputs ranging from efforts used to achieve business goals, its optimization, cash flow, how financial resources are used to provide services or manufacture goods for profit, use and wastage of raw materials, and its economy through buying, processing, and storing until delivery.
Almost all criteria utilized for quantifiable measurements are included in this information, such as applying time standards, stock data, balance sheet data, finished goods inspection results, stock available for sales, machinery utilization data, current assets, and so on.
Projection stage
This phase investigates the measurements that are used to achieve corporate objectives. Forecasts are created using statistical knowledge such as significance, likelihood, confidence, standard deviation, sample size, and correlation.
Following that, plans are established in accordance with the forecast. In the current scenario, a comprehensive prediction plan is thoroughly examined from all conceivable outcomes such as procedures and existing policies, capability and appropriateness of equipment and personnel, organizational structure, and so on. Plans can be changed if necessary.
Selection stage
After thoroughly evaluating all of the proposals, the best one is chosen and implemented during this phase. As a result, the system that the management believes is ideal for attaining business objectives is implemented.
Observation stage
The selected method, strategy progress, and performance are all monitored regularly during this phase. The system must have characteristics such as automaticity, dependability, and adequateness. Adequacy in this context means that data must be precise, neither too large nor too little; it must be adequate in carrying all important information required.
Comparison stage
During this phase, work progress is examined and compared to a predetermined plan to find any discrepancies. The nature of the departure determines whether it is classified as large, minor, or any other type of deviation.
Action stage
Based on the deviation found during the comparison phase, additional action points are established. Strategies are put in place to increase capacity and performance, or to make any forecast changes to ensure optimal performance.
Advantages of management by exception
- It decreases the number of financial and operational results that management must review, making better use of their time.
- This concept empowers employees to take their approaches to obtain the company’s budgeted outcomes. Management will only intervene if there are exceptional circumstances.
- Managers can devote their whole focus and concentrated efforts to significant problems now that they are free of ordinary tasks.
- Managers can conduct an in-depth analysis of the job due to the minimal workload.
- Management by exception increases management activity and control.
- It facilitates easy access to previous trends and efforts.
- It forecasts management opportunities and issues that may develop in the future.
- This method involves both qualitative and quantitative efforts.
- It reduces the number of financial and operational results that management sees.
- It enables lower and subordinate workers to put their ideas into action in order to attain the desired result.
Disadvantages of management by exception
- It is based on previous outcomes to which current data is compared. As a result, if the historical data is incorrect, current decision-making may be affected.
- It necessitates a thorough investigation, observation, and reporting system, which necessitates the hiring of a financial analyst to create summaries and reports and present them to management, necessitating the hiring of additional personnel.
- The system will not tell you until the problem happens, thus it is remedial rather than preventive.
- It is unable to assess human behavior. As a result, it can be difficult to put into practice at times.
Conclusion
Management and planning are essential in human life and the life of every organization. Now that you have understood key management and planning techniques, I’ll love to hear from you. Kindly include your observations, questions, and suggestions in the comment box below.







This is very exsustive and enlightening. This
Thank you, sir.