Alert! How Website Defacement Can Wreak Havoc on Your Small Business!

Website defacement is the modification of the appearance or content of a website without the approval of the owner.
As a small business, it is essential to ensure that all of your digital assets are secure. Unfortunately, website defacement is a growing problem and can cause serious damage to your business.
In this post, I will explore what is website defacement including;
- The origins of website defacement
- How it occurs and the perpetrators
- The effects it has on small businesses, and
- Safety tips to guard against it.
If you are a web designer, a small business owner, a website owner, a blogger, etc, this article is for you. If you are ready to gain knowledge that will assist you and your business, let’s go.
Table of Contents
What is website defacement?
Have you seen the movies Face-off and Ruby Ring where the face of the actors was switched?
In Face-off the face of John Travolta was exchanged for the face of Nicolas cage. Similarly, in Ruby ring, the face of Anna was exchanged for that of her sister Yana.
The effect was that both lived opposite lives filled with lies and deceit to those that loved them.
As the above movies signified, the same is applicable to website defacement. It tends to remove the original content of a website and replace it with other content.
Website defacement is a type of cyber attack in which unauthorized individuals access a website, modify its content, and replace it with their own. This type of attack is known as website vandalism, or “hacking”. It is a malicious act that is typically done for political, religious, or personal reasons.
This is usually accomplished through hacking or exploiting security vulnerabilities in the website’s underlying software or server. The attacker’s goal is often to spread political or social messages or to damage the reputation of the website’s owner.
Popular website defacement attacks
To give you a clearer understanding, take a look at the following news on website defacement attacks.
Georgia’s websites attack
A massive web defacement attack in the country of Georgia defaced about 15,000 websites that resulted in the offline of 2000 websites. The attack was targeted at government websites, tv stations, newspapers, banks, and court sites. It was so significant that it affected the website of the president of Georgia. (Nicole Lindsey, Nov. 2019)
UK NHS website defacement
On April 18, 2018, BBC News reported the defacement of the UK National Health Service (NHS) website, leaving a message.

The website hosts data from patient surveys, and GP surgeries.
Attack on ODIN Intelligence site
Techcrunch reported the defacement of the ODIN Intelligence website by hackers on 15th Jan. 2023. ODIN Intelligence provides technology and tools for law enforcement and police department.
The message left on the website by the hackers read:

Data from ODIN’s site was exfiltrated as a result of the hack. (Zack Whittaker, Jan. 2023).
Defacement of Ukrainian websites
On Jan. 15, 2022, Hackers News disclosed the massive defacement of the Ukrainian government websites. According to the news, no fewer than 70 websites operated by the Ukrainian government went offline for hours.
It was noted that the attack exploited a security vulnerability in Laravel-based October CMS. However, the content of the sites was not altered.

With the above insights and examples, you should clearly understand what is website defacement and what it looks like. You can visit The Hackers News website to learn more about the activities of hackers and defaced websites.
Website defacement is a serious problem and can have a number of negative consequences for small businesses. It can lead to the loss of customer trust and reputation. It can also cause financial losses due to lost sales and disruption of business operations.
Though small business websites are not primarily defaced as seen from the above examples, you ought to be careful. The website to be defaced depends on the interest of the attacker.
Origins of website defacement
Website defacement has been around since the early days of the World Wide Web. Its first documented instances date back to the 1990s. Hackers would alter the appearance of websites to display messages or images.
It was initially used as a form of protest against governments and corporations. However, in recent years, website defacement has become more popular as a form of cybercrime.
As the internet has evolved and become more widespread, the techniques used for website defacement have become more sophisticated. Though the basic concept remains the same: to manipulate the content of a website without the owner’s permission.
The perpetrators of website defacement are typically hackers or individuals who are motivated by financial gain. They can be motivated by anything from political or religious beliefs to personal grudges, to financial gain.
How website defacement occurs
Website defacement occurs when an attacker gains unauthorized access to a website’s server or content management system (CMS) and modifies its content.
This is often done by exploiting security vulnerabilities in the website’s software, and server configuration, or by using stolen login credentials.
Hackers can exploit known vulnerabilities in web applications and server software. They can also capitalize on human errors such as weak passwords or lack of authentication measures.
Once the attacker has gained access, they can make changes to the website’s appearance or content. They can alter text, add images, or replace the website’s homepage with a message of their own.
The attacker may also upload malicious code or malware that can compromise the security of the website’s server and its users.
Website defacement can occur through several means, including:
SQL Injection (SQLi):
Injecting malicious code into a website’s database through a vulnerability in its code. SQL injection is a method of attack that uses malicious SQL code to manipulate backend databases. Using SQLI, data that is not meant to be displayed can be accessed.

A successful attack can lead to effects that are detrimental to your business. These can include:
- Illegal access to user lists,
- The deletion of entire tables, and,
- obtaining administrative rights to a database
Each of these attacks can lead to the loss of customer trust in the business in addition to financial losses.
There are three types of SQLi including in-band, inferential, and out-of-bound SQLi. For example, an SQL query such as this:
SELECT CustomerName, CustomerTel, CustomerAddr
FROM CUSTOMERS
WHERE CustomerID = 999 OR 1=1
If injected into a database can return all the customers’ names, phone numbers, and addresses in the database.
One way to prevent SQLi attacks is by including input validation in your codes. Because this is not a full-proof solution, you should employ a web application firewall (WAF) to filter out SQLi.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
Injecting malicious code into a website that is then executed by unsuspecting users. Cross-site scripting usually targets the users of a web application. It is a process of injecting malicious code into a vulnerable web application.
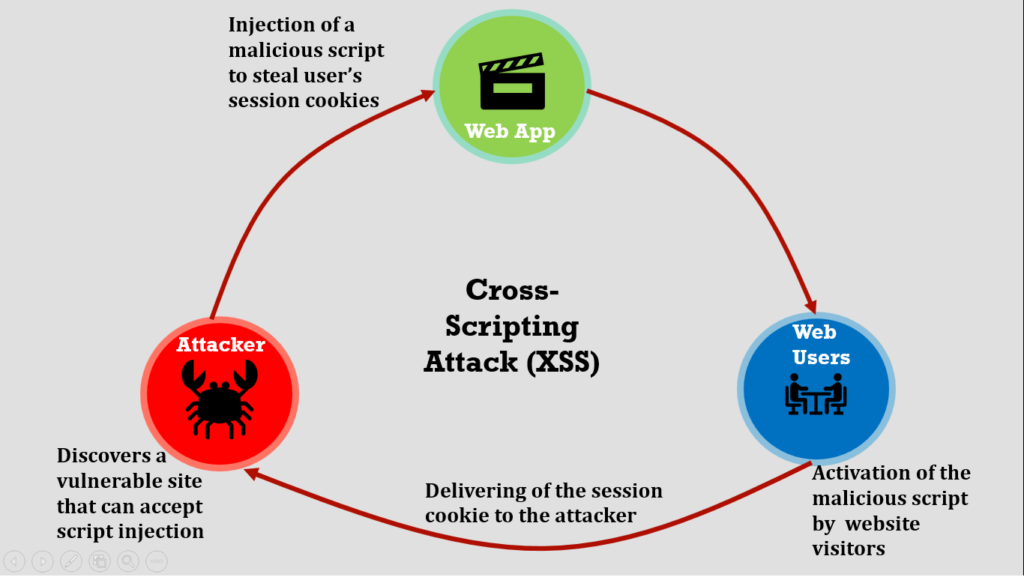
XSS is dangerous and can harm a business including:
- compromising a user account
- modification of page content and activation of the trojan horse program
- impersonation of a user if session cookies are revealed
- misleading a user to ignorantly submit their private data
With the web application firewall, you can prevent your website and web apps from XSS attacks.
Malware infections and attacks:
Attackers can dispatch malicious software to infect individuals and organizations’ computers and networks.
The software will take advantage of flaws in legitimate software (such as browsers or plugins) that can be hijacked.
If such attacks are successful, they can lead to data theft, extortion, or the disabling of network infrastructure.
Similarly, WAF, two-factor authentication (2FA), and backdoor shell protection are common ways to protect against malware attacks.
Unsecured Login Credentials:
Attackers can use stolen or guessed login credentials to access a website’s backend and make changes.
An unsecured login refers to a login process that lacks proper security measures to protect user credentials. Because the login detail is not secure enough they cannot prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
When a login credential is not secure, it becomes vulnerable to attacks such as brute force, dictionary, and phishing attacks. These attacks can result in the theft of login credentials and the compromise of personal and sensitive information.
Users should practice safe online behavior and be vigilant for phishing attacks and security threats that could compromise their login credentials. Also, the use of 2FA can be effective to prevent unauthorized login.
Domain Name Server (DNS) hijacking:
DNS hijacking, also called DNS redirection, is a DNS attack in which users are unintentionally sent to malicious websites. This is done through DNS queries that are wrongly resolved.
Attackers either install malware on user PCs, seize control of routers, or intercept or hack DNS connections to carry out the attack.
DNS hijacking can be used for phishing or pharming, in which the attackers
- display unwelcome advertisements to make money
- displaying fake versions of sites users access and stealing data or credentials
- control a user’s DNS requests by gathering data, and returning advertisements when a user accesses an unrecognized domain,
Several Internet service providers (ISPs) use a sort of DNS hijacking. Also, the government can use it to redirect users from sanctioned websites to officially approved sites for censorship.
As a site owner, you can use two-factor authentication when accessing the DNS registrar, and implement client lock or DNSSEC to avoid DNS hijacking.
Outdated Software:
Websites running outdated software are more vulnerable to attacks, as security patches and updates are no longer available.
To prevent website defacement, it is important to keep software and server configurations up-to-date. Also, you should implement strong security measures such as
- regularly changing login credentials,
- using secure protocols (e.g. HTTPS), and
- using a web application firewall (WAF).
With the above, you can keep your website safe for your business and customers.
In some cases, hackers may also use social engineering techniques to gain access to accounts or websites.
Social engineering involves using deception or manipulation to get someone to reveal confidential information or take action that could lead to a website being defaced.
Who are the perpetrators of website defacement?
Website defacement is typically carried out by individuals or groups of individuals who are motivated by political, religious, or financial gain.
These hackers are often well-versed in computer programming and have access to sophisticated tools and techniques. With these tools, they can gain unauthorized access to websites.
For example, a hacker under the name VandaTheGod was discovered by researchers at Check Point to have vandalized over 4800 websites. The Brazillian hacker, according to The Hacker News is motivated by government sentiments.
Similarly, the Iraqi hacker identified as Pro_Mast3r defaced a website that belongs to the Trump Organization in 2016. From the message, the motive was antigovernment.
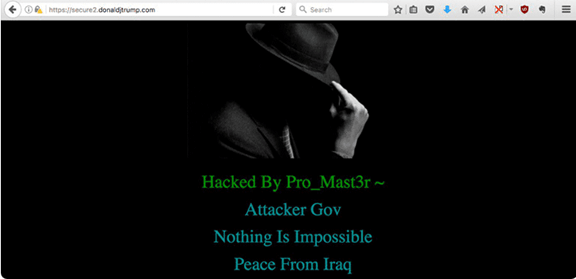
The motivation behind website defacement may vary. It could be a form of protest against a government or corporation, or it could be motivated by financial gain. In some cases, hackers may also be motivated by personal grudges or a desire to damage a company’s reputation.
Effects of website defacement on small businesses
As a small business owner, Blogger, or website designer, you should know the implication of the defacement of a website.
Website defacement can have serious consequences for your small business. Even if you don’t have a business website, consider the reasons you should safeguard your online presence from hackers.
Loss of reputation:
A defaced website can harm the reputation of your small business, causing potential customers to lose trust in the company. This can lead to a decline in sales and a negative impact on the brand.
Financial loss:
Small businesses rely on their websites to generate revenue. For example, my website is a source of revenue through the sale of digital products and ads. Assuming the website is defaced, it may be taken down for an extended period of time. This will lead to a loss of potential sales.
Technical difficulties:
Of a true, defacing a website can cause technical difficulties and disruption of the normal functioning of the site. This can result in the loss of data, slow performance, or the need for costly repairs.
Legal issues:
In cases where a website defacement is illegal, a small business owner may face legal action. This can result in further financial loss, as well as damage to the company’s reputation.
Decreased customer confidence:
Let’s look at it this way if you visit a website that Google gives you a risk alert what will you do? Even if you’ve been visiting the site before, you’ll trade with caution. The same is applicable to every other person.
A defaced website can make customers feel that their personal information and data are at risk. This can result in a loss of confidence in the business, and potentially, a loss of customers.
SEO damage:
Google usually blacklists websites that are potentially at risk. Being a search engine giant, blacklisting your website means that your website will not appear in SERP.
Because your website is defaced, search engines such as Google, Bing, Yandex, etc can penalize your site. This will result in a lower search engine ranking and reduced visibility.
Consequently, your business will be negatively impacted, and its ability to reach potential customers through organic search reduced.
Loss of valuable data:
Depending on the motive of the attackers, a defaced website can result in the loss of valuable data. Valuable data sorted by attackers include customer information, sales reports, and business-critical information.
Attackers who want to extract information can do so, or delete valuable data if they are not able to extract them.
Increased costs:
In addition to the direct financial loss caused by a defaced website, there may also be indirect costs. Such costs include the need to hire professionals to repair the damage and improve the website’s security.
Reduced competitiveness:
When your website is attacked, it would most likely appear unprofessional. This will make it less competitive in comparison to other businesses in the same industry. This will negatively impact the business’s ability to compete for customers and sales.
Decreased employee morale:
A defaced website can cause stress and frustration for employees, which can result in a decrease in morale and productivity.
Website defacement can have significant and long-lasting effects on a small business. It’s important for small businesses to take the necessary precautions to prevent such an attack. Also, a plan should be put in place in case such cases occur.
Solutions to website defacement
In the case you or one of your clients encounter the issue of defaced website, what would you do?
The best solution to website defacement is to take preventative measures to ensure that your website is secure. This includes implementing strong authentication measures, such as two-factor authentication, and regularly updating software and applications.
It is also important to ensure that your website is hosted on a secure server and that your website is backed up regularly. This will ensure that you can quickly restore your website in the event of an attack.
To mitigate the risk of website defacement, it is important to take a multi-layered approach. Some solutions include:
Regular Backups:
Regularly backing up your website can help you quickly restore the site in the event of an attack. This will minimize downtime and minimize the impact of the attack.
Use Secure Web Hosting:
There are many web hosting companies out there. Usually, you may consider the hosting providers that save you cost. Always cross-examine the features provided by your chosen hosting company. Ensure that they offer security features such as automatic security updates, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
Keep Software Up to Date:
Also, it’s your duty to ensure that the software used to build and run your website is always up to date. Attackers often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software.
Implement Strong Passwords:
Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts related to your website, and enable two-factor authentication where possible.
Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF):
It is a best practice to implement WAF on all your websites. A WAF can help to protect your website against attacks by analyzing incoming traffic and blocking malicious requests.
Monitor Your Website:
Regularly monitor your website for any signs of defacement, such as changes in content or appearance. If you suspect an attack, take immediate action.
Educate Your Team:
Train your team on basic cybersecurity practices. For example, creating strong passwords and avoiding phishing attacks. This will reduce the risk of accidental security breaches.
Work with a Cybersecurity Expert:
Consider working with a cybersecurity expert to conduct regular security assessments, implement security measures, and provide ongoing support.
It is important to keep in mind that no single solution can fully protect against website defacement. By implementing multiple security measures, you can reduce your risk and ensure that your website is as secure as possible.
Tips to prevent website defacement on WordPress sites
In as much as the above solutions are applicable to all sites. You can take the following basic measures if you are using CMS to create websites.
Employ the least privilege principle (POLP)
Always restrict access to your website by granting only relevant privileges to users. By restricting access to your websites, you lessen the possibility that a hostile user could cause harm.
I only grant the contributor privilege to authors and writers that create content for my websites.
Thus, avoid granting administrative access to your website. Give users, including webmasters and IT employees, only the permissions necessary to carry out their duties.
Avoid using the admin email and default admin directory.
Never use the default name for your admin directory. Hackers will try to access it because they are aware of the default names for all popular website platforms.
This is one of the security measures I learned early when I started managing WordPress websites. As a beginner, I used the default admin user for several months. I know that many beginners make the same mistake.
The default admin email addresses should also be avoided. Hackers would attempt to exploit them via phishing emails or other techniques.
Use only a few plugins and add-ons
On platforms like WordPress, Drupal, or Joomla, the more add-ons you use, the higher the risk you run into software flaws.
Avoid installing unnecessary plugins, especially, the plugins you may not ordinarily need. Also, keep all website plugins up to date, carefully maintain them, and promptly install security updates.
Avoid displaying error messages
Avoid providing comprehensive error messages on your websites. They can assist attackers by exposing the vulnerabilities of your website.
Impose a file upload limit if you provide such a service
Most membership websites allow users the privilege to upload files. This makes it simple for malware to infiltrate your internal systems.
If you must provide such a service to your users, make sure that no user-uploaded files have executable permission. Also, if you can, scan all user-uploaded files for viruses and impose file upload limits.
Ensure that your website has SSL/ TLS
All website pages should always have SSL/TLS enabled, and links to unprotected HTTP resources should be avoided.
All user communication is secured when SSL/TLS is utilized consistently throughout your website. It helps to thwart several different Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks that could be exploited to deface your website.
The importance of website security
In my last 10 years of designing and managing WordPress websites, I’ve not encountered website defacement issues. But I’ve grown in knowledge to understand the importance of implementing appropriate security measures in WordPress websites.
This knowledge has helped me overcome security bridges that could have left my client’s websites vulnerable.
Website security is important to every small business. Do not neglect the size of your business today, it can grow tomorrow, and security loopholes will find you. If the loophole results in website defacement, be assured that it will affect your business negatively.
Therefore, it is important that you take appropriate security measures to secure your websites.
Website security is important to your small business for the following reasons:
It’s important to Secure customers’ data:
Small businesses often collect and store sensitive information from their customers, such as personal information, payment information, and login credentials. If this information is compromised, it can lead to identity theft, financial losses, and damage to the business’s reputation.
It helps in maintaining brand reputation:
A security breach on a small business’s website can damage the company’s reputation and reduce consumer trust. This can have a significant impact on the business’s bottom line, as customers may take their business elsewhere.
It will also help your business avoid legal liabilities:
As discussed above, website defacement may cause a business to face legal liability. Especially, when they fail to protect the personal information of their customers.
The protection of consumers’ information is crucial; this is why there are laws in the EU and US. For example, the EU has the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the US has the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
These laws require businesses to take specific steps to protect customer information.
It helps Ensure that your business progresses without obstructions:
Website defacement can result in downtime, which can negatively impact the business’s operations and revenue. By taking steps to secure the website, small businesses can minimize the risk of downtime and ensure business continuity.
By securing your website you can protect intellectual property:
Small businesses usually rely on their websites to promote and sell their products or services.
If there is a security breach it can result in the theft of proprietary information. Information such as source code, product designs, and marketing plans, if stolen can harm your business’s competitiveness.
Conclusion
In this article, I discussed website defacement and how it affects small businesses. Measures on how to prevent its occurrence were also discussed.
Now it’s your turn to respond to us. What do you think about a defaced website and how long it takes to restore the site?
What other measures do you think are potent to protect websites from being defaced? Which measures have you used, and what worked best? If there are questions you would want to ask, kindly ask or respond using the comment box below.







Recent Comments