Sustainable Web Design Trends 2025: What You Need to Know

As we approach 2025, the intersection of web design and environmental consciousness has become more critical than ever. Sustainable web design is evolving and is being adopted by businesses and organizations.
With the internet’s carbon footprint projected to account for 8% of global electricity demand by 2030, sustainable web design is no longer a luxury but a necessity.[1]
In 2025, businesses and developers may embrace eco-friendly practices to reduce energy consumption and waste. By adopting lightweight coding, optimizing images, and prioritizing mobile-first designs, the web design industry is paving the way for a greener digital world
This comprehensive guide explores how sustainable web design is reshaping digital experiences while reducing our environmental footprint.
Data centers is now consuming approximately 1% of global electricity and generating 0.3% of all CO2 emissions.[2] Therefore, the need for sustainable web design practices has never been more pressing.
Let’s delve into the key sustainable web design trends that will shape the digital world in the coming years.
The Sustainable Web Design Revolution: What’s Driving Change?
Due to climate change, the web design industry is experiencing a transformative shift towards sustainability. This revolution is being driven by the urgent need to reduce the environmental impact of our digital lives.
Key factors include the following:
- increasing awareness of the internet’s carbon footprint,
- advancements in energy-efficient technologies, and
- growing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions.
- reducing data transfer
- optimizing server efficiency
These changes are setting new standards for web design that not only improve performance but also contribute to a greener planet.
This section explores the factors driving the sustainable web design revolution.
Environmental Impact Metrics
Environmental impact metrics are tools that help measure the environmental footprint of a website. These metrics can assess various aspects, including energy consumption, carbon emissions, and resource usage.
Understanding the environmental footprint of web design is crucial for driving sustainable practices. Environmental impact metrics help quantify the energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with websites and digital services.
These metrics typically include the amount of electricity used by data centers, the CO2 emissions generated by server operations, and the overall energy efficiency of web design components such as images, videos, and code.
By monitoring these metrics, designers can identify areas for improvement, implement more eco-friendly practices, and reduce the digital carbon footprint. Tracking and reducing these metrics not only benefits the environment but also enhances website performance and user experience.
- Average webpage size has grown 544% since 2010: According to the HTTP Archive, the average page size has grown from around 803 KB in 2010 to approximately 2,484 KB in 2023.[3] This growth is driven by the inclusion of larger media files, more sophisticated JavaScript, and additional HTML elements.
- Mobile data traffic expected to reach 282 exabytes per month by 2025: Mobile data traffic is projected to grow significantly, with estimates suggesting it could reach around 282 exabytes per month by 2025.[4] This increase is due to the growing number of mobile broadband subscriptions and the rising consumption of data-intensive applications.
- Websites with optimized images reduce carbon emissions: Optimizing images can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of websites. Studies have shown that efficient image compression and optimization can lead to substantial reductions in energy consumption and carbon emissions.[5] Optimized images require less data to be transmitted and processed, which in turn reduces the energy consumption of servers and networks.
Sustainable web Design: Key Industry Shifts
The web design industry is witnessing several pivotal changes as it embraces sustainability. One major shift is the increased focus on energy efficiency, with designers prioritizing lightweight coding and optimized media to reduce server loads.
There’s also a growing trend towards green hosting solutions, where companies choose providers that use renewable energy sources. Additionally, the industry is adopting more inclusive design practices, ensuring websites are accessible to all users, which often leads to more streamlined and efficient designs.
These shifts are driven by a combination of regulatory pressures, consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions, and technological advancements that make sustainable design more achievable.
Carbon-Aware Development
Carbon-aware development is an approach to software engineering that focuses on minimizing the carbon footprint of digital services. This involves designing and deploying software in a way that leverages greener energy sources and reduces energy consumption during times of high carbon emissions.[6]
By using tools like the Carbon Aware SDK, developers can measure the carbon emissions of their software and make informed decisions about when and where to run their applications.
This can include running energy-intensive tasks during times when renewable energy sources are more prevalent, such as when the wind is blowing or the sun is shining. Companies like UBS and Vestas have already adopted this approach to build greener software solutions.
Elements of carbon development
In the context of Carbon-Aware Development, these three elements play crucial roles:
- Real-time Carbon Intensity Monitoring: This involves tracking the carbon intensity of electricity in real time. By having access to this data, developers can make informed decisions about when and where to run their applications to minimize carbon emissions.[7] For example, they can schedule energy-intensive tasks during times when the grid is powered by renewable energy sources. Octopus Energy offers a real-time carbon intensity monitoring app. This app provides users with real-time data on the carbon intensity of the grid, helping them decide the best times to use energy-intensive appliances like washing machines or electric vehicle chargers.
- Adaptive Loading Based on Grid Energy Sources: This approach adjusts the load on servers based on the carbon intensity of the grid. When the grid uses more renewable energy, the system can increase its load, and when the grid uses more fossil fuels, it can reduce its load. This helps in optimizing energy consumption and reducing the overall carbon footprint. Optimal Adaptive Heuristic Algorithm is an example of adaptive loading. This algorithm optimizes energy usage by scheduling household appliance usage during times when the grid is powered by renewable energy sources. It helps in reducing peak-to-average demand ratios and electricity bills while maintaining user comfort.
- Automated Performance Optimization Tools: These tools automatically optimize the performance of applications to reduce energy consumption. By improving the efficiency of code and infrastructure, these tools can significantly lower the carbon emissions associated with running applications. Dynatrace is a popular automated performance optimization tool. It provides AI-powered analytics to monitor and optimize application performance in real-time. Identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks ensures applications run efficiently and meet user expectations
Together, these elements help create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to software development and deployment.
Minimalist Design Evolution
Minimalist design has evolved significantly over the years, tracing its roots back to early 20th-century art movements like Bauhaus and De Stijl. These movements emphasized simplicity, functionality, and the use of basic geometric shapes.[8] Over time, minimalist design expanded into various fields, including architecture, interior design, fashion, and technology.
Companies like Apple have championed minimalist design in their products, promoting sleek, user-friendly interfaces. This approach has been adopted in web design, where simplicity enhances user experience and reduces cognitive load.
Reduced Dependency on Heavy Media Files:
In minimalist web design, reducing dependency on heavy media files is essential for both aesthetic simplicity and environmental sustainability. By minimizing the use of large images, videos, and animations, websites can significantly lower their data transfer requirements. This not only speeds up page load times, enhancing user experience but also reduces the energy consumption of servers and networks. Techniques such as compressing images, using vector graphics, and optimizing media files ensure that the necessary visual elements are maintained without overwhelming the design or the environment.
Strategic Use of System Fonts:
Using system fonts strategically is another hallmark of minimalist design. System fonts are pre-installed on most devices, which means that they don’t need to be downloaded when a user visits a website. This reduces page load times and data usage. Additionally, system fonts are designed to be highly readable and compatible across different browsers and devices, ensuring a consistent and user-friendly experience. By opting for system fonts over custom web fonts, designers can achieve a clean, efficient, and fast-loading site that aligns with minimalist principles.
Simplified User Interfaces Without Sacrificing Functionality:
A core aspect of minimalist design is creating simplified user interfaces (UI) that do not compromise functionality. This involves stripping away unnecessary elements and focusing on the essential components that provide value to the user. Simplified UIs leverage intuitive navigation, clear typography, and ample white space to guide users effortlessly through the site. This not only enhances usability but also reduces cognitive load, allowing users to find information quickly and efficiently. Techniques such as using concise text, clear icons, and logical layouts ensure that even the most minimalist interfaces remain highly functional and user-friendly.
2025’s Most Impactful Sustainable Web Design Trends
As we step into 2025, the web design industry is witnessing a transformative shift towards sustainability. This year, several key trends are emerging, driven by the urgent need to reduce the environmental impact of digital services.
From energy-efficient coding practices to eco-friendly hosting solutions, these trends are setting new standards for creating greener, more efficient websites.
In this section, we’ll explore the most impactful sustainable web design trends of 2025, highlighting how they are reshaping the digital landscape and contributing to a more sustainable future.

Adaptive Dark Mode Implementation:
This involves creating a website or application that automatically switches to dark mode based on the user’s operating system settings or preferences. It enhances user experience by reducing eye strain and saving battery life on devices with OLED screens.[9] Implementation typically involves using CSS variables and media queries to detect the user’s preferred color scheme and apply the appropriate styles.
Progressive Enhancement 2.0:
This approach focuses on building a core, accessible experience that works for all users, regardless of device or connection speed. Then, additional features and enhancements are progressively added for users with more capable devices and faster connections. This can lead to significant performance improvements and reduced energy consumption.
Green Hosting Integration:
Green hosting refers to using web hosting services that are environmentally friendly by minimizing carbon footprints and using renewable energy sources. Integrating green hosting involves choosing hosting providers that use energy-efficient data centers, renewable energy credits, and eco-friendly practices to reduce the environmental impact of running websites.[10]
Intelligent Asset Loading:
This technique involves optimizing the loading of website assets (such as images, scripts, and stylesheets) based on the user’s device, network conditions, and browser capabilities. By prioritizing essential content and deferring non-critical assets, websites can load faster and provide a better user experience, especially on slower connections.
Edge Computing for Sustainability:
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source of data generation (e.g., IoT devices), reducing the need for data to travel to centralized data centers. This can lead to lower latency, improved performance, and reduced energy consumption, making it a sustainable approach for handling large-scale data processing and real-time applications.
By leveraging edge computing, websites can improve performance and reduce energy consumption associated with data transfer.
Practical Implementation Strategies
As sustainable web design continues to gain traction, it’s crucial to understand how to implement these practices effectively. This section will provide actionable insights and step-by-step strategies to help web designers and developers integrate sustainability into their projects.
From choosing energy-efficient hosting solutions to optimizing site performance, these practical approaches will ensure your digital presence is both eco-friendly and user-friendly. By adopting these strategies, you’ll be well-equipped to contribute to a greener web and set new standards for sustainable design.
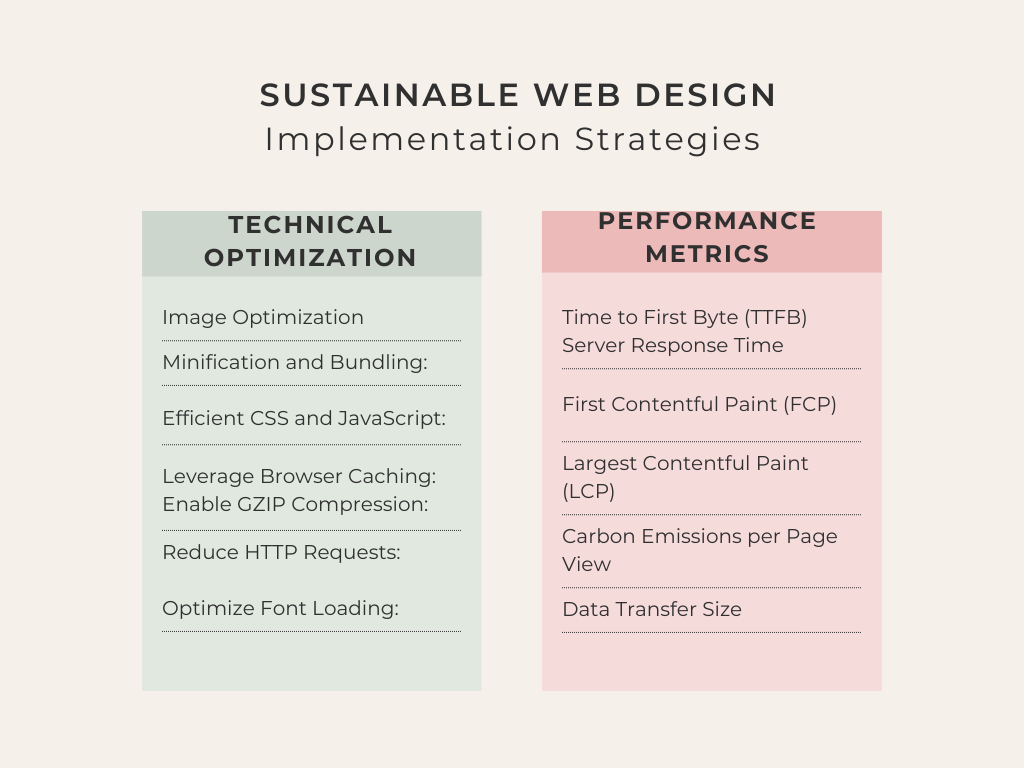
Technical Optimization
Implementing technical optimization strategies is essential for sustainable web design. To ensure optimal performance and minimize environmental impact, consider the following technical optimization strategies:
Image Optimization:
- Compress images without compromising quality.
- Use appropriate image formats (e.g., WebP, AVIF) for better compression.
- Implement lazy loading to defer loading of images until they are about to enter the viewport.
Minification and Bundling:
- Remove unnecessary characters (e.g., whitespace, comments) from CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files.
- Combine multiple files into fewer, larger files to reduce HTTP requests.
Efficient CSS and JavaScript:
- Minimize the use of blocking JavaScript.
- Prioritize critical CSS to render the initial page content faster.
Leverage Browser Caching:
- Set appropriate cache headers to reduce server load and improve performance.
Reduce HTTP Requests:
- Combine files, use CSS sprites, and optimize font loading to minimize the number of requests.
Optimize Font Loading:
- Use fewer font files and prioritize system fonts.
Enable GZIP Compression:
- Compress files before sending them to the browser to reduce transfer size.
Performance Metrics to Monitor
To ensure the effectiveness of optimization strategies, it’s crucial to monitor specific performance metrics.
These metrics help identify areas for improvement and track the impact of changes over time. Here are some key metrics to focus on:
Time to First Byte (TTFB)
TTFB measures the time it takes for the server to respond to a user’s request and send the first byte of data. A lower TTFB indicates a faster server response, which can improve overall site performance and user experience.
First Contentful Paint (FCP)
FCP marks the time at which the first text or image is painted on the screen. A quick FCP ensures that users see content sooner, which can reduce bounce rates and enhance the perception of site speed.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP measures the time it takes for the largest visible content element to load. Optimizing LCP is important for improving user engagement, as it ensures that the main content of the page is rendered promptly.
Carbon Emissions per Page View
Tracking the carbon emissions associated with each page view helps assess the environmental impact of a website. Tools like Website Carbon Calculator can estimate the CO2 emissions generated by a website and provide insights on how to reduce them.
Data Transfer Size
This metric measures the total amount of data transferred from the server to the user’s browser. Reducing data transfer size through techniques like file compression and image optimization can significantly improve load times and reduce energy consumption.
Server Response Time
Server response time measures the time it takes for the server to process a request and return a response. Optimizing server response time through efficient server configurations and reducing backend processing can enhance overall site performance and user satisfaction.
By focusing on these technical optimizations and performance metrics, web designers and developers can create more sustainable, efficient, and user-friendly websites.
Local SEO Integration for Sustainable Web Design
Local SEO integration is essential for ensuring your web design is both sustainable and highly effective in reaching targeted audiences. By focusing on geographic optimization, you can improve site performance, enhance user experience, and reduce environmental impact.
Geographic Optimization
- Region-specific asset delivery: Implementing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to serve assets (such as images, scripts, and styles) from servers closest to the user can significantly reduce load times and energy consumption. This approach minimizes data transfer distances and speeds up content delivery.
- Local server utilization: Utilizing local servers helps to reduce latency and improves load times. By hosting your website on servers located near your primary audience, you can enhance performance and decrease the carbon footprint associated with long-distance data transmission.
- Cultural design considerations: Designing websites with cultural nuances in mind ensures that content resonates with local audiences. This includes using appropriate color schemes, imagery, and content that align with the cultural preferences and norms of your target regions.
- Language optimization: Providing content in the local language of your target audience not only improves accessibility but also boosts SEO rankings. This involves translating and localizing content to cater to different linguistic groups, making your website more inclusive and user-friendly.
Voice Search Optimization
With the rise of voice-activated devices, optimizing for voice search has become crucial for improving accessibility and enhancing user experience. Here are key strategies for voice search optimization:
- Natural language processing: Voice search queries tend to be more conversational and natural. Implementing natural language processing (NLP) techniques helps to understand and respond accurately to these queries, making your website more user-friendly and accessible.
- Question-based content structure: Structuring your content to answer common questions can improve your chances of appearing in voice search results. This involves creating FAQ sections and using headings that mimic the way people speak, ensuring your content aligns with user search patterns.
- Local business schema markup: Implementing schema markup for local businesses helps search engines understand and display your business information more effectively in voice search results. This includes details like business hours, addresses, and contact information, making it easier for users to find relevant local services.
- Mobile-first indexing: With the majority of voice searches conducted on mobile devices, ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is essential. Mobile-first indexing prioritizes the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking, so optimizing for mobile performance is critical for voice search success.
These practical implementation strategies will help you create a more sustainable, efficient, and user-friendly web presence.
Industry-Specific Applications
Recognizing the unique needs and challenges faced by different sectors, this section delves into how these innovative practices can be applied to industry-specific scenarios.
From healthcare to retail, real estate to hospitality, understanding the nuances of each industry allows for the creation of web solutions that are not only efficient and eco-friendly but also highly effective in reaching and engaging local audiences.
By embracing these strategies, businesses can enhance their online presence, improve user experience, and ultimately drive growth in a sustainable manner.
E-commerce
Low-carbon checkout processes
Implementing low-carbon checkout processes involves optimizing the entire purchase pathway to minimize energy consumption. This includes streamlining code to reduce the number of server requests, employing energy-efficient payment gateways, and utilizing green hosting services to lower the carbon footprint of each transaction.
Sustainable product highlighting
E-commerce platforms can promote sustainability by clearly highlighting eco-friendly products. This can be achieved through dedicated categories for green products, using badges or labels, and providing detailed information about the sustainability credentials of each product.
Green shipping calculators
Integrating green shipping calculators allows customers to select shipping options based on their environmental impact. These calculators can provide information on the carbon emissions associated with different shipping methods, encouraging customers to choose more sustainable options.
Eco-friendly packaging options
Offering customers the choice of eco-friendly packaging is another way e-commerce platforms can promote sustainability. This can include using biodegradable, recyclable, or reusable packaging materials and providing information on the environmental benefits of these options.
Media and Entertainment
Adaptive streaming quality
Implementing adaptive streaming quality ensures that video content is delivered at the optimal resolution for the user’s device and internet connection, reducing unnecessary data transfer and energy consumption.
Carbon-aware video delivery
Media platforms can adopt carbon-aware video delivery by dynamically adjusting the delivery of content based on the carbon intensity of the electricity grid at any given time. This can help minimize the environmental impact of streaming services.
Efficient content caching
Utilizing efficient content caching techniques can significantly reduce the energy required to deliver media content. By storing frequently accessed content closer to users, platforms can reduce the need for long-distance data transfers and decrease overall energy consumption.
User-controlled quality settings
Providing users with the option to control the quality of the content they stream allows them to choose lower resolutions that consume less data and energy. This can be particularly effective for users who are conscious of their environmental impact.
Corporate Websites
Sustainability reporting integration
Corporate websites can integrate sustainability reporting by regularly publishing detailed reports on their environmental impact, goals, and achievements. This transparency can help build trust with stakeholders and demonstrate the company’s commitment to sustainability.
Carbon footprint dashboards
Implementing carbon footprint dashboards on corporate websites allows companies to monitor and display their carbon emissions in real time. These dashboards can provide insights into energy consumption patterns and help identify areas for improvement.
Green hosting certificates
Displaying green hosting certificates on corporate websites can showcase the company’s commitment to using eco-friendly hosting services. These certificates can be obtained from hosting providers that use renewable energy sources and follow sustainable practices.
Environmental impact statements
Publishing environmental impact statements on corporate websites can provide a comprehensive overview of the company’s sustainability initiatives. These statements can include information on the company’s carbon footprint, resource usage, waste management, and other environmental metrics.
Future-Proofing Your Sustainable Web Design
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the importance of sustainable web design becomes increasingly significant. Future-proofing your web design involves implementing strategies that not only address current sustainability challenges but also anticipate and adapt to future technological advancements and environmental considerations.
In this section, we will explore innovative approaches and best practices to ensure that your web design remains resilient, efficient, and eco-friendly in the face of changing trends and emerging technologies.
By adopting these forward-thinking strategies, you can create a web presence that is both environmentally responsible and prepared for the future.
Let’s explore the key elements of future-proofing your sustainable web design:
Emerging Technologies
- Quantum Computing Integration: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize web design by solving complex problems more efficiently than classical computers. As this technology matures, integrating quantum computing into your web infrastructure can significantly reduce energy consumption and improve processing speed. This can lead to more sustainable and efficient web solutions.
- Bio-inspired Design Patterns: Drawing inspiration from nature, bio-inspired design patterns leverage principles observed in biological systems to create efficient and sustainable web designs. This includes using algorithms that mimic natural processes, such as the growth of plants or the behavior of animals, to optimize resource usage and minimize environmental impact.
- Carbon-neutral Frameworks: Adopting carbon-neutral frameworks involves utilizing development tools and methodologies that aim to achieve net-zero carbon emissions. This can be accomplished by incorporating energy-efficient coding practices, optimizing resource usage, and offsetting any remaining carbon emissions through initiatives such as reforestation or renewable energy projects.
- Green AI Implementation: Implementing green AI involves designing and deploying artificial intelligence systems that prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability. This includes using AI models that are optimized for low energy consumption, leveraging AI to optimize other aspects of web design, and utilizing renewable energy sources to power AI infrastructure.
Best Practices for 2025 and Beyond
- Regular sustainability audits: Conducting regular sustainability audits helps identify areas where your web design can be improved in terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact. These audits involve assessing the entire web infrastructure, from hosting services to content delivery, and implementing changes to reduce the overall carbon footprint.
- Carbon budget allocation: Allocating a carbon budget involves setting limits on the amount of carbon emissions your web design can produce. By monitoring and managing this budget, you can ensure that your web operations remain within sustainable limits. This approach encourages the adoption of energy-efficient practices and the use of renewable energy sources.
- Green hosting partnerships: Partnering with green hosting providers that use renewable energy sources and follow sustainable practices can significantly reduce the environmental impact of your web design. Look for hosting providers that offer green certifications and have a proven track record of sustainability.
- Environmental impact reporting: Regularly publishing environmental impact reports provides transparency and accountability for your sustainability efforts. These reports should detail the steps taken to reduce carbon emissions, the progress made towards sustainability goals, and the overall environmental impact of your web design. This not only builds trust with stakeholders but also demonstrates your commitment to sustainability.
By embracing these emerging technologies and best practices, you can future-proof your web design, ensuring it remains sustainable, efficient, and adaptable to the ever-changing digital landscape.
Implementation Checklist
To successfully integrate sustainable web design strategies, it’s essential to have a comprehensive and structured approach.
This Implementation Checklist serves as a practical guide to ensure that all critical aspects of sustainable web design are addressed. From initial planning to ongoing maintenance, this checklist will help you stay organized and focused on achieving your sustainability goals.
By following these steps, you can create a web presence that is not only efficient and user-friendly but also environmentally responsible.
Let’s explore the key elements that should be considered during the implementation process.
Technical Requirements
- Implement adaptive loading strategies
- Optimize image delivery
- Configure proper caching
- Enable compression
- Set up monitoring tools
Design Requirements
- Create dark mode variations
- Optimize typography
- Reduce animation usage
- Implement efficient layouts
- Design for accessibility
Content Requirements
- Optimize for voice search
- Create local variations
- Implement schema markup
- Develop sustainability statements
Measuring Success
Implementing sustainable web design strategies is just the beginning. To ensure that your efforts are effective and continuously improving, it’s crucial to have robust metrics and evaluation processes in place.
This section on Measuring Success will guide you through the key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluation methods that can help you track the impact of your sustainability initiatives.
By regularly assessing your progress, identifying areas for improvement, and celebrating your achievements, you can maintain momentum and drive ongoing success in your sustainable web design journey.
Let’s explore the essential tools and practices for measuring and achieving sustainability goals.
Key Performance Indicators
- Carbon emissions per visit
- Page weight
- Server response time
- User engagement metrics
- Conversion rates
- Local search rankings
Tools and Resources
- Website Carbon Calculator
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- Green Web Foundation Directory
- Local SEO tracking tools
- Carbon awareness APIs
Conclusion
Thanks, we’re done. Give me a compelling conclusion, with a call to comment
Certainly! Here’s a compelling conclusion with a call to comment:
Conclusion
In an era where digital presence is paramount, embracing sustainable web design is no longer just an option—it’s a responsibility.
By implementing the strategies and best practices we’ve discussed, you can create a web experience that is not only efficient and user-friendly but also environmentally conscious.
Whether you’re optimizing for local SEO, integrating voice search capabilities, or leveraging emerging technologies, every step taken toward sustainability contributes to a greener and more resilient future.
As we look ahead, the commitment to sustainable web design will continue to shape the way we interact with the digital world. Let’s work together to build a future where technology and environmental responsibility go hand in hand.
Have thoughts, questions, or experiences to share? We’d love to hear from you! Comment below and join the conversation on how we can make the web a more sustainable place for everyone.
[1] Sustainable Web Design Trends Reshaping 2025: Why They Matter?
[2] Data centres & networks – IEA
[3] https://www.pingdom.com/blog/webpages-are-getting-larger-every-year-and-heres-why-it-matters/
[4] https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report/dataforecasts/mobile-traffic-forecast
[5] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43979-024-00103-w
[6] Carbon Aware SDK | Carbon Aware SDK
[7] Real-time data can help to track and reduce emissions from electricity sector – Analysis – IEA
[8] Minimalist Design: History, Foundations, Evolution, and Key Characteristics