The Importance of Effective Communication to a Small Business

Communication is the transmission of information from one location to another. A communication process may be faced with barriers that could mar the purpose of the communication.
Effective communication is one that eliminates hitches and ensures that the purpose of communication is achieved. Every business, large or small requires effective communication to succeed. Hence communication is an important aspect of business management.
In this article, I will discuss communication as it affects businesses including:
- The meaning and types
- The process and importance of good communication channels
- The channels and barriers to effective communication
If you are a business owner, an employee, a student, or a researcher, don’t call it quits. Let’s explore the meaning and the communication process.
One of the most crucial life skills to learn is how to communicate effectively. The definition of communication is the exchange of information for the purpose of knowing more.
It can be accomplished verbally (via conversations), in writing (books, websites, and periodicals), and visually (using graphs, charts, and maps). It can also be accomplished through non-verbal (body language, gestures, pitch of voice, and tone). These several forms of communication are all crucial Soft Skills for a successful career.
The transfer of information is the standard definition of communication. The phrase can either be used to describe merely the message being transmitted or the area of the study looking into such transmissions.
What is Communication?
Communication is the act of transmitting and receiving information through written or oral language, written or graphic representations (such as infographics, maps, and charts), signs, and signals. Communication is defined as “the creation and exchange of meaning,” to put it another way.
Information is sent and received during communication, which can take place face-to-face, over a communication device, or between individuals or groups of people. Senders must transfer their thoughts or encode a message in order for communication to take place. The receiver is the individual who gets this communication, and it is up to the receiver to decipher or interpret it. Although it seems straightforward, this is more difficult.
Language is a system of signs and symbols that is unique to the society that speaks and writes it. A grasp of common concepts and a common language are necessary for effective communication. Additionally, it’s crucial to keep in mind that a recipient can perceive a message differently than the sender intended.
The Latin term communicate, which means to share or make common, is the origin of the English word “communication” (Weekley, 1967)[1]. The process of comprehending and exchanging meaning is referred to as communication (Pearson & Nelson, 2000)[2].
The relationship that incorporates participant contact is at the heart of our investigation into communication. With its emphasis on the procedure for efficiently understanding and sharing another person’s point of view, which we’ll explore in-depth throughout this text, this definition is helpful to us.
The process is the definition’s first important term. Because it changes, a process is a dynamic activity that is challenging to describe. Assume you are alone in your kitchen, contemplating something. You briefly converse with the person who enters the kitchen (let’s pretend it’s your mum). What’s different now?
Imagine that in addition to your mother, there is now a stranger you have never met, and they are attentively listening to everything you say, almost as if you were giving a speech. What’s different now? You might alter your viewpoint, and you might pay closer attention to what you say. You might need to reconsider what you are saying in light of your mother’s and the stranger’s comments or reactions, who are essentially your audience.
“To understand is to perceive, to interpret, and to tie our perception and interpretation to what we already know,” is the second important concept (McLean, 2003)[3]. What picture comes to mind when a friend tells you a tale about falling off a bike? Your companion now gestures toward the window, where you can see a motorcycle on the ground. Understanding the words and the ideas or things they allude to is crucial to effective communication.
The word sharing follows. Sharing refers to carrying out an action with one or more other persons. You can collaborate on an activity, like when you put together a report together, or you can both use and benefit from a resource, like when you and your coworkers split a pizza. When you communicate your thoughts, feelings, ideas, or insights to others, you are sharing. You can communicate with yourself when you experience “Aha!” moments when something finally makes sense, when thoughts spring to mind, when you reflect on how you feel about something, or when you solve a problem. This process is known as intrapersonal communication.
Finally, meaning is what we communicate about. The word “bike” can refer to a motorcycle as well as a bicycle. We can determine the word’s common meaning and comprehend the message by looking at the context in which it is used and by asking questions.
The communication process
Below is the explanation of each communication process component:
The sender
The message is created by the sender or contact and sent to the recipient. He is the first contact and the source.
The message
It is something the sender has created for reference—an concept, information, opinion, truth, feeling, etc.
Encoding the message
Before transfer, the sender’s communication is encrypted using symbols like words, images, touches, etc.
The medium of communication
This is how the coded message is delivered to the receiver. Either verbally or in writing, the message can be delivered.
Recording the message
It involves altering the signals that are sent by the sender. The recipient hears the message after it has been recorded.
The receiver
Since you are the last in the chain, the message you sent has already been delivered. Only after the message is appropriately understood and used by the recipient do we say that the communication’s goals have been met.
The noise
Noise refers to any limitations imposed during the communication process by the sender, message, or recipient. For instance, a bad phone connection, bad coding, bad recording, a thoughtless recipient, a message that was misunderstood because of discrimination or inappropriate touching, etc.
The feedback
The communication process is finished when the recipient gives the sender confirmation that they received and understood the message.
What is an encoder in communication?
The process of converting information into a format that can be sent to another person or system is known as encoding. The recipient must first decode the message in order to understand it once the sender has encoded it in a way that can be understood by them. Communication needs to be encoded and decoded in order to be effective.
A communication model that explains the communication process is the encoding and decoding model of communication. It starts with the sender employing words, symbols, or other forms of communication to encode the desired message. The recipient then attempts to decipher the message’s significance by decoding it.
The information must first be translated into a form that can be communicated before it can be encoded.
Encoding entails turning the sender’s words or ideas into symbols that the recipient can understand. Then, in order to comprehend the original message, the recipient decodes the symbols.
An encoder is therefore a tool or person who converts data or information into a format that can be understood by a machine or another person. The encoder is the individual who creates and transmits the message.
In communication, an encoder is in charge of converting the message from the sender into a format that the recipient can comprehend.
What is a decoder in communication?
Decoding in communication is the process of translating a coded message into a meaning that can be communicated to the recipients. The communication is encoded by the sender using a code, which the recipient decodes and then interprets. Both verbal and nonverbal communication can be used for this.
Successful decoding requires expertise (say, careful reading or listening to a message). When the message is appropriately decoded, the information will be understood by the recipient. Decoding is the process of interpreting a message that has been encoded by a source using the decoder’s own perspective and background such that the message is concise and obvious.
The decoder is thus, the person or tool that interprets the meaning of the communication that was sent to them. A lot is involved in the process of decoding, including language, skill, expertise, etc.
Types of Communication
There are basically two major types of communication, namely;
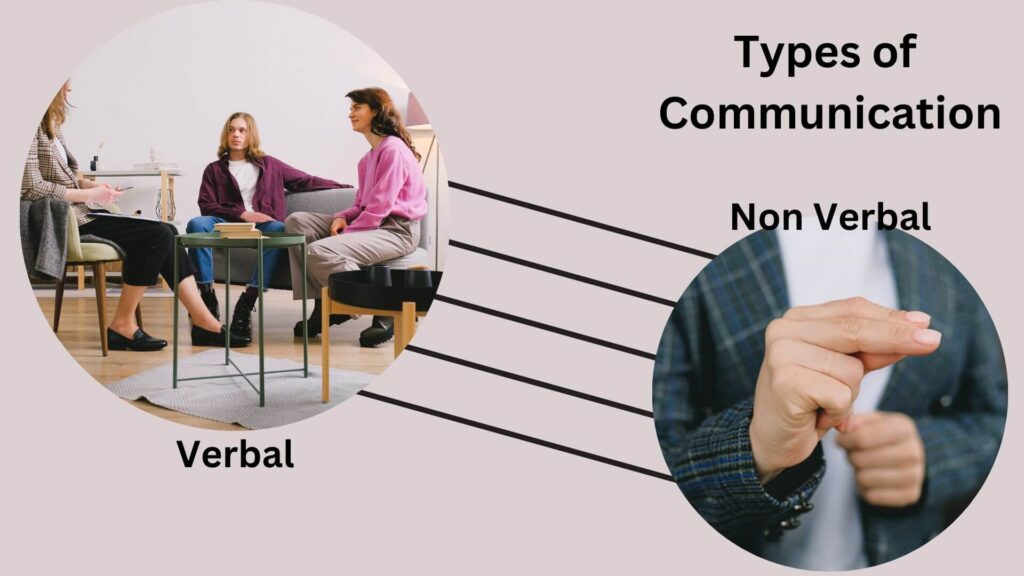
Oral or verbal communication
Oral communication is any form of communication that takes place verbally and sends or receives messages from others. The use of language to convey information orally or through sign language is known as verbal communication. Verbal communication is crucial because it is effective. The use of visual aids to support spoken communication using body language Any verbal, nonverbal, spoken, or written communication is referred to as.
Non-verbal communication
Signs, symbols, colors, touches, bodily parts, or facial traits can all cause it. Using body language, facial expressions, and body language insignificantly to communicate with others. It can be applied both consciously and unconsciously. When you hear an idea or some intriguing or interesting information, for instance, you might smile. When attempting to comprehend the opinions and sentiments of others, open conversation is beneficial.
What is Communication Channel?
Information travels forward, backward, and sideways inside an organization. Communication describes this exchange of information. The organization’s internal communication channels describe how this information is distributed.
Communication channels describe the ways in which information travels both inside and outside of an organization. The flow of information within a corporation is aided via channels of communication.
Written papers and verbal and nonverbal cues are examples of communication routes. Since so much communication takes place nonverbally, some routes may be more efficient than others. Digital technology in the workplace nowadays offers a variety of online communication channels that can link workers from across the globe.
Categories of communication channels in an organization
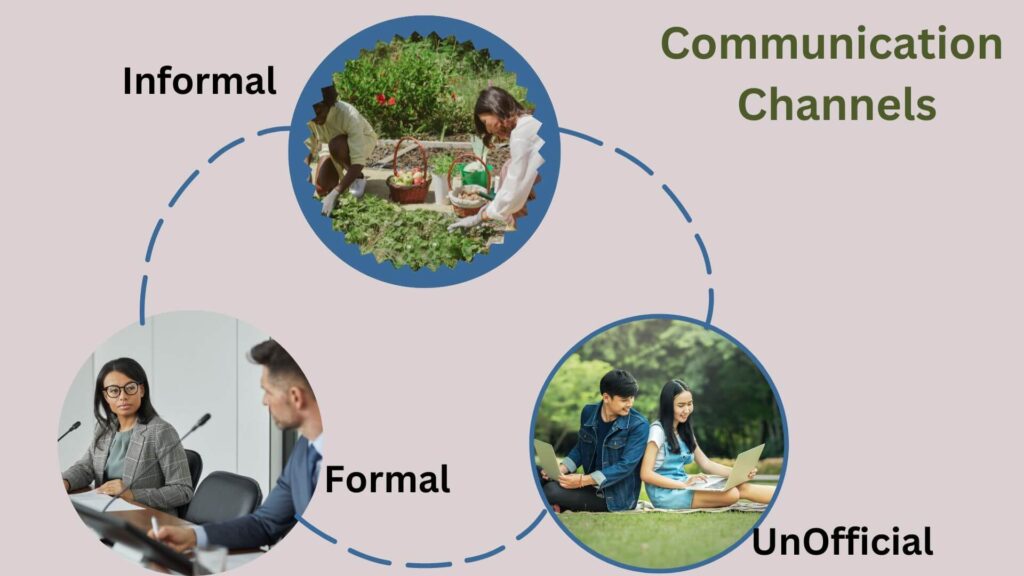
Formal communication channel
It is a method of official communication. Information like an organization’s objectives, policies, and procedures are communicated through a formal communication channel. This kind of channel for communication uses a chain of command for messages. This implies that information is passed down from a manager to his subordinates, who then pass it on to the staff member below them. Company newsletters, business strategies, guidelines, yearly reports, contracts, company-wide communications, board presentations, etc. are a few examples.
Informal communication channel
This is also a formal way of communicating with a somewhat looser norm. This type of communication may not require a sequence of commands or hierarchy. There will be a great deal of formal communication where no such hierarchy or mandate is required, but it will take place within a formal framework. Some examples include desktop conversations addressing questions from team members, lunchtime conversations, and many emails that don’t require formal direction.
Unofficial channels
Good managers will be aware that interpersonal communication can sometimes take place within an organization. Employees may discuss meeting minutes, but they may also bring up sports, politics, or television series.
The “local gossip” within an organization is the unofficial communication conduit. Local gossip is the medium by which rumors are spread. Additionally, people that participate in “rumor mill” conversations frequently establish groups, which results in friendships outside of the organization.
Although information spread through the grapevine may have positive effects, it is more often than not overblown and may frighten workers unnecessarily. An effective manager should be aware of the information being spread through this unofficial communication channel and should take proactive steps to stop the flow of incorrect information.
These communication channels include face-to-face conversations, videoconferencing, audio conferencing, emails, written letters and memos, chats and messaging, blogs, formal written documents, spreadsheets, etc.
What is The Importance of Good Communication Channels in An Organization?
Any organization must prioritize communication. It makes it possible for the information to flow from the highest-ranking management structures to the lowest-ranking employee. It improves comprehension, assisting the organization’s expansion.
Below is the key importance of good communication channels in any organization.
It creates a confident work environment
Improved morale fosters a positive work environment that makes the company successful. By creating a work environment with open communication channels, employees understand their responsibilities and company expectations.
Employees have a better understanding of how to achieve goals, boost employee morale, and increase employee retention. Similarly, open communication channels work to the management’s advantage as they listen to and address employee concerns.
Overall, this form of effective workplace communication ensures that all team members feel valued and accounted for in company decisions.
It motivates employees
Clear communication in a business environment can motivate employees by setting clear and achievable goals. Managers can set clear goals for their employees if they know the parameters of the tasks and the processes required to complete them. Additionally, corporate communications can provide feedback that helps employees improve their workplace performance and grow as industry professionals.
It promotes employee growth and development
A key component of business success is evolving and changing with the market and consumer demand. Here, effective communication within an organization is essential to driving business development and growth and gaining an edge in the market. Open communication channels between employees and management enable employees to exchange ideas, communicate policy changes, and rapidly develop approaches to solve new challenges.
It provides relevant information for team success
Communication in a business environment is critical to ensuring that all employees have the information to do their jobs. Team members have the data, guidelines, or facts they need to do their jobs accurately and insightfully. Therefore, the dissemination of information throughout an organization is essential to maintaining employee productivity and business insight.
It helps in developing a strong management team
Management skills are enhanced when managers use effective organizational communication. From delegating tasks to motivating employees, building employee relationships, and resolving conflicts, management is improved through clear and assertive communication. Additionally, maintaining an open communication channel between managers and their employees promotes practical problem-solving and efficient responses to unexpected problems.
It is essential in maintaining compliance with organizational policies
A formal, documented policy allows an organization to communicate definitive procedures for various workplace scenarios. From employee codes of conduct to disciplinary processes, policies help create consistent expectations, streamline processes, and create a safe and accessible workplace. This method of communication makes all employees feel supported and welcomed. Managers communicate company policies, educate employees about new procedures, maintain open communication channels, and accurately set workplace expectations.
It encourages employee collaboration
When working in teams with common goals, corporate communication helps everyone work together to achieve common results. Communication is essential to creating these collaborative environments, maintaining a shared vision, and turning complex processes into achievable steps. To foster employee collaboration, both formal and informal communication methods are used to allow managers to share important information through appropriate channels and foster spaces for teamwork and open discussion. is important.
It helps in creating a recognizable brand image
Companies maintain established brands. From social media posts to internal memos, a familiar brand image makes your business more recognizable to customers, increases loyalty and drives sales. Maintaining a consistent tone and style throughout communication, therefore, helps promote a unified image of the company. Many large companies have specific branding guidelines to standardize their communications, create their own style on social media, and enhance their professional presence in their industry.
What is a Feedback Loop in a Communication System?
A feedback loop is a process in which some or all of the system’s output is fed back and used as the system’s input. The term was first used in the fields of engineering and electrical engineering.
A feedback loop is a process by which a designer uses the output of a system as input to find causal relationships in the system. Some systems (such as the environment) have many feedback loops, and it can take decades for the effects of human behavior to appear.
In complex systems, feedback loops can hide causality and problems. A feedback loop is defined as a system where the output of the system becomes the input of the next iteration of the system. This simple idea is everywhere.
Human homeostasis, investment banking, thermostats, biological ecosystems, etc. A system that takes processed information and uses it to control or regulate itself can be thought of as a feedback loop.
In business communication, a feedback loop is a loop that facilitates communication between customers and companies. It is the process by which customers leave feedback and allow the company to validate it. Technically, a feedback loop can be described as the process by which system output is fed back into the system.
Feedback loops are important in a business environment because they help companies use customer and employee feedback to develop better services and products.
Positive feedback loop
A positive feedback loop is a self-reinforcing cycle that seeks to amplify the signal passing through it. A perfect example is compound interest in the banking world. In this case, the money in the account can continue to profit as interest is added and compounded further. Each year, the amount in your account will be more than last year, and your total amount will increase rapidly as your account balance gradually increases.
Negative feedback loop
Negative feedback loops react to change and use mechanisms to reduce or reverse the change. A good example of this is a thermostat. When high temperatures are detected, the loop activates air conditioning to reduce temperatures. The thermostat takes a temperature reading every minute, blows cold air until it reaches the ideal temperature, and the cycle ends when the next peak is detected. In general, negative feedback makes the system more stable and adjusts the effect to stay within normal limits.
Advantages of feedback loops
The customer feedback loop is essentially a cross-causal relationship in which both the customer and the brand influence each other. There are several reasons why you need to respond to customer feedback and build a solid feedback loop in today’s market.
It strengthens the existing customer base
Establishing a credible feedback loop can help a company maximize its LTV (lifetime value) of existing customers. The more you maintain your existing customer base, the less pressure you have to find new customers.
It helps to build a better customer-business relationship
Feedback loops drive the best use of such platforms and help companies learn about their customers’ needs and expectations.
It builds trust and loyalty
When brands use customer feedback as a central component of their product and marketing strategy, it opens up multiple opportunities for building lasting business-customer relationships and earning market trust.
It reduces negative feedback
Think about it, as more and more customers strive to leave feedback, you’ll eventually reach a point where customer complaints are greatly reduced.
It helps businesses plan for the future
Well-developed feedback loops can keep companies in check, support market research, and prevent wishful thinking and delusions. In other words, these help marks allow the user to decide which product to launch.
It helps businesses expand their market share
Businesses that are nearer to their customer base frequently increase their market share. This is due to the fact that they have a greater understanding of the problems that consumers encounter, what they anticipate from their goods and services, and which steps in the process they enjoy the most.
To show off your professionalism
Feedback loops offer businesses a great chance to present their professionalism and build a solid online reputation. Additionally, it aids businesses in utilizing word-of-mouth advertising, the most successful type of advertising there is.
Mention some Barriers to Effective Communication
Anything that prevents someone from receiving and comprehending signals sent to them to express their ideas, thoughts, or any other kind of information is considered a communication barrier. The message that someone is attempting to deliver is blocked or impeded by these numerous communication barriers.

There are many obstacles that can stand in the way of good communication. This occurs because the sender’s message might not be received exactly as intended. As a result of the communication exchange, it may get distorted. These various barriers to communication can appear at any point throughout the exchange of information. It could be brought on by workplace prejudice, stereotyping, or generalization.
Below are some of the barriers to effective communication.
Mental barriers
The recipient’s state of mind determines how the message is received. Stress management is an important personal skill that influences relationships. For example, anger is a psychological barrier to communication. When we are angry, we tend to say things that we later regret or misunderstand what others are saying. Also, people with low self-esteem may lack self-confidence and be poor at communicating.
Physical Communication Barriers
With more communication channels available and less technology required, communication is generally easier over shorter distances. Modern technology can often help reduce the collapse of physical barriers, but the strengths and weaknesses of each communication channel should be kept under wraps so that the right channel can be used to overcome physical barriers. need to do it.
Physiological barriers
Physiological barriers can affect the physical condition of the recipient. For example, a recipient with fused hearing may not be able to hear all of the spoken dialogue, especially if there is a lot of background noise.
Language barriers
Language and language ability can act as barriers to communication. However, even when communicating in similar languages, the terminology used in the message can be a barrier if the recipient does not readily understand it.
Attitudinal barriers
Attitude barriers are perceptions that prevent people from communicating well. Attitudinal communication barriers can result from poor management, personality conflicts, struggles for change, or lack of motivation. You have to challenge yourself to overcome the attitude barrier.
Emotional barriers
Emotionally mature people can communicate effectively. On the other hand, those who control their emotions face certain challenges. Effective communication requires the perfect mix of emotion and fact. Emotions such as anger, frustration, and humor can cloud a person’s decision-making ability and limit the effectiveness of communication.
Barriers to cultural communication
As the world becomes more globalized, large offices may have employees from different parts of the world. Different cultures have different meanings for the core values of society. Clothing, religion, food, drink, pets, and general behavior vary greatly from culture to culture.
Therefore, we need to take these different cultures into account when communicating. Many multinational companies offer special courses at the orientation stage to inform people about other cultures and teach them how to be polite and tolerant when dealing with others.
Organizational barriers
As we have seen, there are many ways to communicate at the organizational level. Each of these methods has its own set of problems and limitations that can create barriers to effective communication. Most of these roadblocks are caused by misinformation or a lack of adequate transparency available to employees.
Barriers caused by a perception
Different people perceive the same thing differently. This is a fact that must be considered during the communication process. Knowing your audience’s level of perception is important for effective communication. All messages or communications should be simple and clear. There is no room for multiple interpretations.
Socio-religious and technological barriers
The use of technology is another hurdle. Because technology is advancing quickly, it is become harder to stay up with the most recent advancements. As a result, sometimes technology might act as a barrier. In addition, the cost of the technology might occasionally be exceedingly costly.
The majority of businesses won’t be able to purchase decent communication technology. This becomes a very important barrier as a result. Socio-religious barriers are additional obstacles. A woman or transgender person may encounter various obstacles and problems while attempting to communicate in a patriarchal environment.
Business or industry terminology
Every industry has its own set of specific vocabulary. Although using these phrases can occasionally seem more efficient, it can be perplexing to people outside the industry or with little to no professional experience. You can abstract your messages and make it more difficult for people to understand vital information by using jargon or extremely technical language.
Instead, make an effort to avoid jargon and decipher acronyms. An employee in product development, for instance, might not be aware that the term “KPI” stands for “key performance indicator” or that it’s a value a company evaluates to ascertain how well a corporation is reaching a business aim.
Conclusion
As discussed above, a lot could hinder business communication. And ineffective communication could lead to inefficient business operations which could culminate in business failure.
Now that you know, it is your turn to respond to this article. How do you communicate in your organization? Which channels are effectively used in your organization? What are the barriers that have hindered communication in your organization? Kindly respond or make suggestions using the comment box below.
[1] Weekley, E. (1967). An etymological dictionary of modern English (Vol. 1, p. 338). New York, NY: Dover Publications.
[2] Pearson, J., & Nelson, P. (2000). An introduction to human communication: Understanding and sharing (p. 6). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill.
[3] McLean, S. (2003). The basics of speech communication. Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.