What is staffing – Effective Staffing Process for your Business
Staffing is important to every business that has a mission and desires to grow. In order to meet the purpose of your business, other people’s input matters. Though this depends on the level of business activities undertaken by your business.
Thus, it is necessary to understand what is staffing, the recruitment process, and the basics of production management.
Therefore, this article will help you begin the process as you’ll learn staffing, recruitment process, authority, and contract. Let’s quickly begin with what is staffing.
What is Staffing?
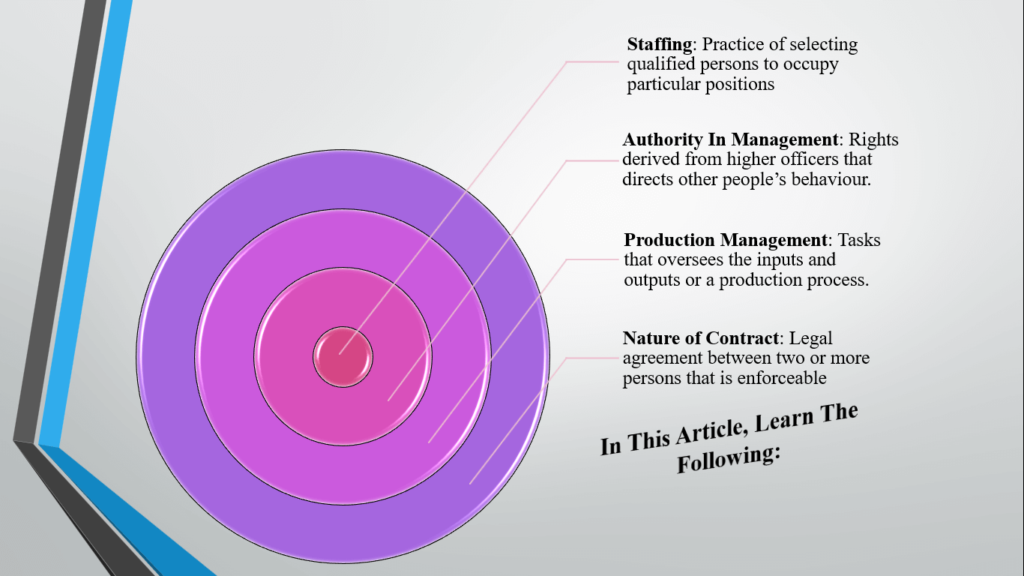
Staffing is the practice of selecting qualified applicants from within the organization or business for particular positions. In terms of management, staffing refers to the process of hiring new employees after assessing their qualifications and assigning them specific job tasks in accordance.
A managerial task called staffing entails finding, using, and keeping qualified and competent workers to fill every position within an organization, from the top to the bottom echelons. In more precise terms, staffing refers to assigning the ideal candidate to the ideal position.
Finding the ideal candidate with the necessary skills or experience and hiring them to fill a position or role in the process of staffing.
Organizations can hire, use, and retain a staff that is both sufficient in size and high quality to improve the effectiveness of the company. In management, staffing is the process of hiring new employees and assessing their knowledge and skills before assigning them to specific job responsibilities in accordance.
In workers’ retrenchment, what do you consider natural FIFO (First-in First-out) or LIFO (Last-in First-out)
Retrenchment can be brought on by a variety of circumstances, such as the more automated society we live in or a financial crisis that may persist for a short while or last for a long time and accidentally force businesses to reorganize their corporate structures. Although the legal system is aware of the necessity for cutbacks, it cannot be used as a trump card to fire people.
Naturally, the FIFO in retrenchment means laying out the older staff in the organization in the order of their employment.
Sometimes these older staff do not care for certifications and training programs to improve their skills. thus, it is natural to lay them off in that order when their contributions to the organization are compared with the new in-takes.
LIFO aims to honor the dedication of workers who have devoted a significant amount of time to their employer.
Retaining effective and capable personnel is smart on the side of the employer and in the best interests of a firm because a period of retrenchment is an unpredictable time for both the employer and the employee.
The LIFO principle is intended to provide a sound defense against treating employees differently during layoffs. It is most relevant and contentious when there are several employees, all doing the same job, who are interchangeable.
What do You Understand by the Principle of Management’s Ability to Pay In Management Labour Wage Negotiation?
In its broadest definition, the term “wages” refers to any financial remuneration that an employer makes to his employees in exchange for the services they provide. Therefore, wages also include other perks like financial support, family allowance, and relief pay. However, in a more restricted sense, wages only refer to performance wages or wages proper and are the cost of the labor used in the manufacturing process.
There are principles governing the implementation of wages and salaries in an organization. Amongst them is the principle of management’s ability to pay.
The principle states as follows:
There should be a clear strategy in place to guarantee that variations in job requirements, such as skill effort, responsibility, or job or working environment, as well as mental and physical requirements, are the basis for disparities in remunerations.
In general, salaries and earnings should be at a level that is reasonably consistent with the labor market’s norms. The most typical criterion is the labor market one. The plan needs to clearly define the difference between jobs and employees.
However, the organization should not agree with the employees on the pay wages that it cannot pay. Every remuneration negotiation should be based on the organization’s ability to meet the staff’s obligation. Such a policy is superior to the industry pay standard which may put the company in a default position.
To ensure coordination, uniformity, and justice in employee compensation, organizations must create policies that serve as broad principles. The solutions to the problems raised by the prior discussion of the compensation philosophy are reflected in the pay policies. For instance, adhering to the pay-for-performance attitude necessitates factoring the findings of the performance review into the pay adjustment.
What Steps are Necessary for the Recruitment of New Staff?
Finding and hiring qualified candidates to fill unfilled positions in a firm is the recruitment process. A recruiter, the human resources division, the hiring manager, or the department manager frequently handles recruitment.
The procedures businesses take to find and select new applicants are referred to as the recruiting process. Businesses that seek the top candidates for available positions must have a successful recruiting procedure. Knowing how to maximize recruitment is crucial if you work in human resources.
The 7 steps of the recruiting process are as follows:
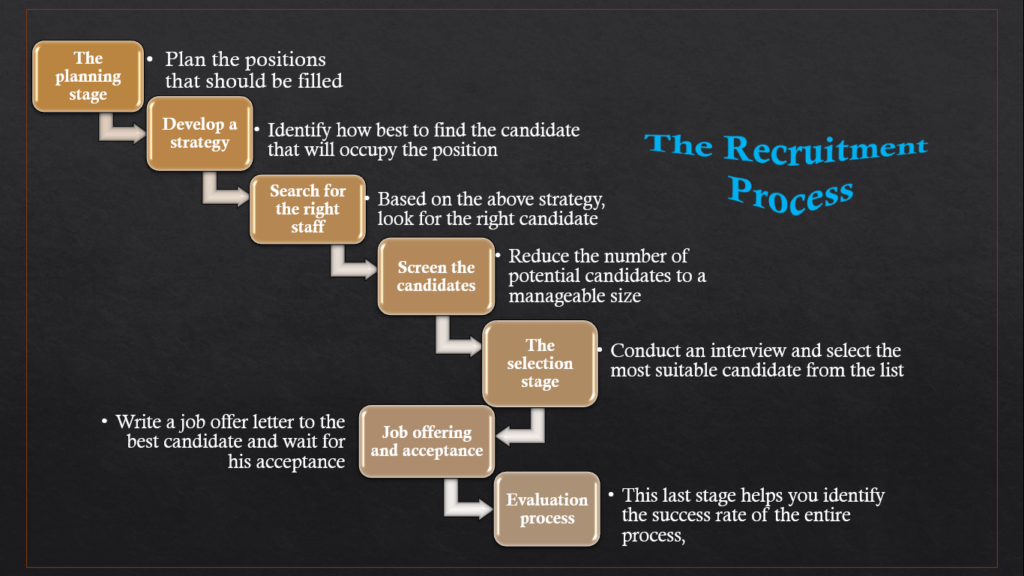
Planning of positions
You identify the positions that need to be filled and create the job descriptions for each position during the planning stage. Job descriptions describe the tasks and obligations an employee is expected to carry out as well as the education and training required to complete the work.
How you will discover candidates to fill the post is described in the recruitment plan. At this point, the hiring team decides if the candidates should have prior experience or if they will receive on-the-job training. This has an impact on the salary, the qualifications the employer intends to present in the job description, and any potential training resource requirements.
Development of recruitment strategy
How you will discover candidates to fill the post is described in the recruitment plan. At this point, the hiring team decides if the candidates should have prior experience or if they will receive on-the-job training. This has an impact on the salary, the qualifications the employer intends to present in the job description, and any potential training resource requirements.
Publishing vacancies or searching for the right staff
The process of actively seeking employment candidates is known as the searching stage. A lot of businesses combine internal and external sources to find people.
Utilizing staff referrals and past candidates, the hiring process might be internal. Any recruiting strategy that involves searching outside of the company, such as employment agencies, advertisements, campus recruiting, direct recruiting, and professional groups, falls under the category of external hiring sources.
Screening of prospective candidates
The act of reducing the pool of applicants to those who will be interviewed is known as the screening process. This entails separating unqualified individuals from those that seem like a good fit by evaluating resumes and cover letters. You should take into account each candidate’s training, credentials, job history, and professional development.
Interviewing and selection
The interview is often conducted in person, however, if the candidate is not nearby, it may be done through video conference. The managers meet with a select number of the top applicants during this round. Depending on the number of applicants, the size of the company, and the level of competition for the position, there may be more than one in-person interview required for the interview process.
Offering the job and onboarding of best candidates
The next action is formally extending the job offer to your top choice. An offer letter that details the start date, salary, working hours, and expected performance should be sent. If you’re working with a recruitment agency or search consultant, they should make the job offer.
If the prospect accepts the offer, you ought to provide thorough onboarding to formally introduce your new hire. The onboarding process teaches your new hire about the working environment, how to get ready for the job, and what to anticipate on their first day.
Evaluation of the process
Analyzing the success of your recruiting strategies is the last step in the hiring process. You can assess the efficiency of the recruiting tactics, your happiness with the prospects you recruited, and any improvements to the process by carefully evaluating the procedure.
What are the Parameters for Calculating the Performance of a Staff?
The performance of an organization is always measured by the performance of the employees working in the organization. The performance of the organization can be measured by the revenue it is earning and the profits that it is enjoying. This is quite significant and is not hidden from anyone.
You may evaluate the effectiveness and productivity of your workforce using employee performance measures. They serve as benchmarks for evaluating an employee’s performance to that of their coworkers and your expectations.
Some of the metrics used to measure employee performance are:
Close Rate
The ability to meet with prospects and make sales is an important skill for sales associates. Agent close rate represents the percentage of leads that are converted to customers.
Defect Rate
The general assessment of employees working in manufacturing or repair areas. Error rate measures the percentage of products that employees are working on that contain errors.
Error Rate
Similar to Error Rate, Error is a metric that evaluates employees based on the mistakes they make on the job. Consider applying the error rate metric in situations where the error is not an accurate description of the error.
Upsell Rate
Many companies place great importance on offering additional products or services to their customers’ purchases. For example, when buying a new cell phone, a salesperson may try to sell you a case, wireless charger, or extended warranty. A seller wins an upsell when a customer purchases one or more additional items.
Review Score
Employees may be reviewed and rated in various settings. The annual executive performance review may include a numerical or written evaluation of the employee’s performance during the evaluation period.
Average Sales
The sales representative’s average sales provide valuable information about the effectiveness of sales to customers.
Attendance
An employee’s attendance record is a good indicator of poor performance. Since it is common for employees to include vacation and sick leave in their contracts, employees should not be penalized for using these vacations. However, employees who are consistently absent or late may indicate a lack of engagement.
One-time contacts
Similar to call duration, measuring contacts over a while (usually weekly or monthly) shows how much effort a sales rep puts into reaching a lead.
Generated leads
For a marketer, lead generation is one of his most important tasks. While the quality of leads is important, employers also benefit from evaluating the number of leads generated by marketers.
Unit production
Workers in a manufacturing or packaging function are often evaluated based on the total units they produce during a shift.
Gross sales
Sometimes supervisors are interested in looking at an employee’s gross sales rather than qualitative statistics such as average employee sales or sales growth. As a quantitative statistic, Total Sales does not take into account other metrics such as profit margins, but it can indicate a salesperson’s overall selling ability.
What is Line Authority in Management?
A person receives the right to work in an organization based on authority, which is a particular permit gained from their higher officer. It is positional and inherent in the job. It is essential to managerial duties. Without authority, no one can carry out their responsibilities fully.
In management, authority is the ability to make decisions that direct other people’s behavior. The establishment of an organization is aided by authority delegation. No one person can perform all the tasks required of them in an organization. Delegating authority and adhering to the division of labor rules are necessary to complete the task on time.
Regardless of the type of organization they work in, managers in practice undertake essentially the same tasks because they are all concerned with getting the job done through people.
A person receives the right to work in an organization based on authority, which is a particular permit gained from their higher officer. It is positional and inherent in the job. It is essential to managerial duties. Without authority, no one can carry out their responsibilities fully.
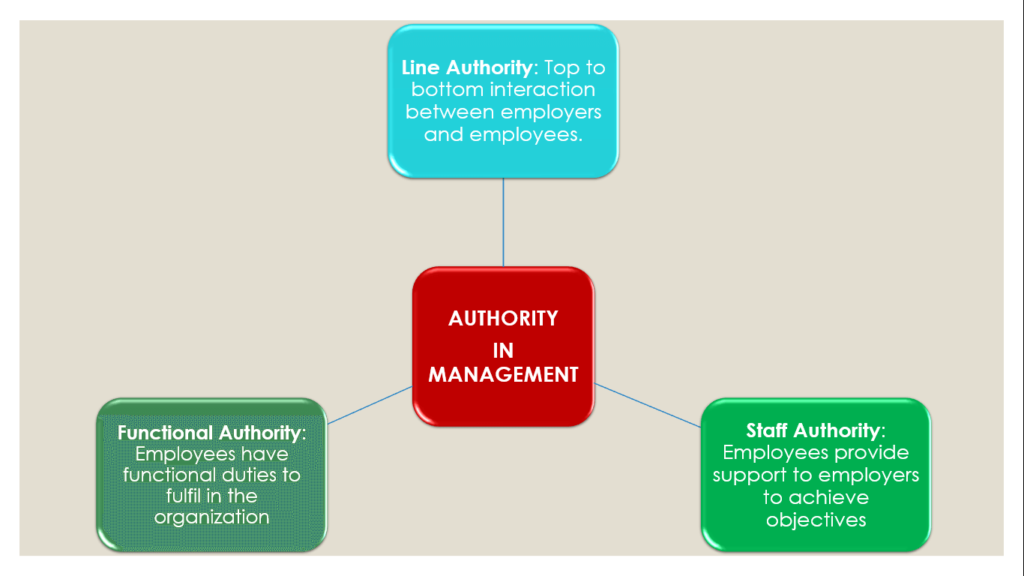
There are three different types of authority: line, staff, and functional authority.
Line Authority
An employee’s work is managed with the use of line authority. It takes the shape of a top-to-bottom interaction between employers and employees. As a result, the line manager sometimes makes decisions without consulting anybody else.
In some instances, the word “line” is used to distinguish line managers from staff managers. As a result, the manager whose duties directly contribute to the accomplishment of organizational goals is referred to as a line manager.
It is that authority that a superior exercises over his subordinates to accomplish the primary objectives of the organization. The superior issues orders and instructions to his subordinates to complete the tasks.
Line authority defines the relationship between superior and subordinate. It is direct supervisory authority from superior to subordinate. Managers who supervise operating employees or other managers have this authority. This authority flows downward in an organization directly from superior to subordinate.
Functional authority
Functional control is sometimes referred to as functional authority. Also included are the personnel and line-of-business components of HRM. Because the personnel manager uses his or her specific authority to plan the personnel activities. As the supreme executive’s right arm in this situation, the HR manager fulfills his duties.
What is staff authority in management?
Literally, staff implies a stick carried in the hand for support. In the context of management, it implies those elements that help the line authorities to function effectively in accomplishing the primary objectives of the enterprise.
The staff managers are in charge of staff authority. The line and staff nature of any manager’s responsibilities is determined by the organization’s objectives. The moment the organization’s size keeps growing. The line managers then believe they are unable to do their duties using their current skills.
Additionally, expertise and knowledge has not been updated appropriately As a result, staff authority is created for the employees whose primary duty is to help. Along with providing assistance, counsel, and lessening the line managers’ workload.
Staff provides advice, assistance, and information to line managers, and they are distinguished into three categories namely, personal, specialized, and general staff. They reduce the burden of line authorities and they too have the right to command and extract work from their subordinates.
According to Henri Fayol “staff are an adjunct, reinforcement and a sort of extension of line manager’s personality.”
What is the Nature of Information in an Organization?
Information is traditionally thought of as human-to-human exchanges. However, technical advancements rather than the growth of mathematical reasoning have led to the expansion of this idea throughout history.
The term “information” today refers to an abstract idea that is based on Claude Shannon’s information theory, which was developed in the middle of the twentieth century. However, the main factor in the term “bit” becoming so well recognized is computer technology. In addition, phrases like virtual reality, which depend on the processing of information, are becoming commonplace.
One of the best parts of human life’s essentials is information. Information is regarded as the lifeblood of study in the modern world.
Profit making organizations
In profit-making organizations, information can be useful in the following areas:
Security:
Security threats and vandalism are issues that most modern businesses deal with. To gain a competitive edge, technology can be utilized to protect financial data, private management choices, and other proprietary information.
Digital Marketing & Advertising:
The ability of businesses in many sectors to advertise their goods and services online is one of the key uses of information technology in business. Nearly all websites have advertising surrounding their primary content.
Product Creation:
Companies can recognize shifting client demands more quickly with the aid of information technology than with conventional research and response methods. In the end, this enables the business to react swiftly to modifications in the external environment. The time to market for innovative products can be sped up using information technology.
Operating Effectiveness:
Information technology may also assist organizations in understanding their cash flow requirements and in conserving precious resources like time and real estate. Business leaders may better grasp everything from controlling inventory expenses to delivering goods thanks to inventory management technologies.
Online Transfers of Payment:
The quickest way to complete any commercial transaction right now is through the use of digital money transfers between two or more parties. Compared to the custom of mailing paper bills and collecting payment afterward, this is significantly less expensive.
Connection with Clients:
Information technology helps businesses create and manage client interactions better. To gain additional experience, the customer relationship management (CRM) system takes into account the complete relationship between the company and the customer.
Web-based Storage:
Computers are very universally used in business to store data. Excel and Office are two apps that can assist you to keep track of the figures. Accounting software like Tally may store company data like sales, tax records, and industry-specific data.
Globalization:
Market integration into the global economy is referred to as globalization. Locally and globally, businesses benefit from information technology growth. Companies can employ linked technologies to communicate while outsourcing their non-core tasks to local small companies.
Worldwide Communications:
Most contact in the twenty-first century is done via email. E-mail communication is more expedient and affordable than letter writing. The greatest benefit of using technology for communication is speed. The pace of communication has accelerated. how quickly you launch your business.
Non-for-profit making organizations
In NGOs, information is mostly used for the following;
Budgeting:
One of an NGO’s most crucial components is the budget. Data can be used to ascertain the requirements and preferences for the programs of an organization when creating a budget. The more information a company has about its spending patterns, the simpler it is to distinguish between what is essential and helpful and what is not.
Fundraising:
Data can assist an NGO in raising money. With data, financial planning for an organization can be done considerably more effectively. This is crucial when asking for donations from investors because they are the ones who will most likely be providing them with funding in the future. Targeting potential contributors and informing them of an organization’s accomplishments and offerings should always take priority,
Monitoring activities:
Initiatives within an organization must be continuously monitored to ensure that their objectives are being accomplished and that progress is being achieved as intended. This monitoring becomes considerably more difficult without adequate tracking methods in place, especially for complicated projects and programs. An NGO can benefit from data in this process by gathering important statistics, publishing the findings of social media monitoring, and even providing feedback on operations that have been undertaken.
Operational simplification:
The process of operationalizing an NGO can be challenging, but data offers a wealth of information that supports standardized procedures and efficient operations. When operations are more streamlined, they can:
- maximize the number of services given while minimizing costs.
- Save time while reducing wasteful spending or work.
- enable the determination of what processes are most efficient and effective.
Management Involves Profit-Making Organizations and Non-Profit-Making Organizations
Both businesses and NGOs require effective management to grow and sustain their goals in the long run.
We’ve discussed the need for organizational management above, however, NGOs require good management too. This is because good management will help NGOs in the following ways.
For proper accountability to the donors:
Since the majority of NGOs rely solely on funding, it is crucial to have reliable accounting systems in place.
For securing the future:
An organization’s future is determined by its current financial situation. NGOs should choose sustainable financial use similarly. This merely means that NGOs should invest money in their current projects while considering the long term.
To eliminate fraud and theft:
Fraud, theft, and other unlawful activities like improper resource utilization have grown commonplace among NGOs. Firm checks are essential, for limiting such illicitness and preventing the exploitation of resources. These problems are easily resolved with thorough financial planning, coordination, and control.
For making effective decisions:
NGOs that practice excellent financial management are better able to allocate resources, raise money, mobilize funds, and carry out other tasks. The proper amount of money can be invested at the right location with the help of good decision-making abilities. As a result, money is used effectively and efficiently.
For the purpose of achieving goals:
Each NGO is driven by a specific set of policies and procedures that are tied to its overarching goals. The authority makes decisions with the effective accomplishment of its stated aims and objectives in mind.
For increasing credibility:
Managing finances is a matter of abilities and strategies, which should preferably vary periodically. NGOs with strong financial management improve their reputation, increasing their worth and credibility.
To increase the fund-raising efforts
Increasing fundraising efforts is necessary because the majority of NGOs rely entirely on donations. Financial resources that are well-organized aid in boosting fundraising efforts by providing a general notion of the amount of money that is already accessible and how much money still needs to be raised. As a result, workers have a good understanding of the expected amount and can arrange their fundraising efforts accordingly.
What are the Goals of Profit and Non-profit Making Organizations?
Because they can aid a team, department, or organization in identifying its short-term and long-term objectives, business goals are a crucial component of the strategic planning process. You can choose a variety of company objectives, such as increasing revenue or enhancing customer happiness.
Business goals
Some examples of business goals include.
- Profit maximization
- Long-term survival in the market
- Increased market share
- Sales maximization
- Brand loyalty, etc
Non-for-profit organization goals
Such organizations are created to impact the lives of the less privileged in society. Some of the goals of such organizations include:
- To increase exposure and awareness among the public
- To raise funds to carry out developmental projects
- To recruit volunteers to impact the lives of the society
- To create a corporate partnerships with government and businesses
- To increase the channels of donation
- To win local and international awards for recognition and accomplishment
What is Production Management?
Production management is a term for a collection of tasks that include organizing, coordinating, overseeing, managing, and making decisions regarding the inputs and outputs of a production process. Organizational divisions are often held accountable for all industrial operations, including their number, cost, and quality.
The production management should ensure that the company’s production strategy, which calls for the use of specific technologies and the attainment of pre-established targets for production mixes, unit costs, quality, and production capacity, is successfully implemented. In general, it coordinates, supervises, and manages the individuals or teams in charge of production management, equipment maintenance, quality control, and inventory management.
One aspect of business management is production management. It differs from functions that are focused on other dimensions, such as marketing, sales, distribution, finance, and information systems, in that it focuses on the transformation process of inputs and raw materials into the company’s finished products.
What are the steps in establishing a small-scale business?
All prospects and sources must be well-developed before starting a firm. A strong basis is created by having a solid foundation. Every big firm had its humble beginnings. All factors should be considered before beginning a small business or any internet business. For this, a methodical approach is ideal. As an entrepreneur, a lot is invested.
Numerous events might have an impact on your business. Sound business judgment, thorough preparation, and legal obligations are just a few of the many responsibilities that entrepreneurs must handle. These issues make up the character of your small firm.
The steps you can take include:
- Conduct market research: Aside from a select few, most business owners lack access to wealthy people or epiphanic moments. Some people even try to come up with the original golden idea. It’s time to put your small company idea into action once you have it all planned out in your head.
- Write a business plan for the intended idea: A business plan must be written once you’ve done all the required research for your small firm. A solid business plan will enable your small firm to operate effectively and serve as a guide for all of your decisions.
- Get a suitable business location: The choice of your company’s location is crucial. It alone will determine your company’s performance and the tax rules and regulations that apply to it.
- Choose a suitable business name: It is necessary to secure your company’s name once you’ve chosen it because it will function as its distinctive identity. The business name must be registered.
- Secure the necessary funds to start the business: The first financial action to take is to finance your small business. A business can obtain financing through a variety of methods. However, determining the precise amount of cash required is an essential first step. A clear image of the money your small-scale business needs will be revealed in the previous phase, which involved determining the cost of business funding. An entrepreneur is free to select the method of funding in light of this.
- Select a business structure: You can now choose a business structure for your proposed business – sole proprietorship, partnership, or limited liability. Business structure is the deciding factor for tax payments, provision of funds, and division of responsibilities. before registering your business with the state it is necessary to conclude with your business structure.
- Register the business entity: Your business must be registered to be recognized as a distinct legal entity. You do not, however, need to register your business if you are using your name as your business name. Where and how a firm must be registered depends heavily on its location and organizational structure. The majority of small enterprises only need to register their company name with state and municipal authorities. A business owner might receive legal advantages, tax advantages, and personal liability protection by registering their company.
- Get the necessary tax identification numbers (TIN): It is through this number that your business can pay all the taxes, get permits and licenses, and open a business bank account.
- Open a business or corporate account: This is dependent on the kind of business you want to run. Go to your desired bank with the necessary registration documents and open a corporate account.
- Open your business for operation: Other things may be involved including preparing your office and production equipment, etc. When all is set, start your business operations.
What is an industrial arbitration court?
The Industrial Arbitration Court, which was later replaced by the Industrial Relations Act (Cap 136, 2004 Rev Ed), was passed in 1960, creating the Industrial Arbitration Court (IAC). The court was established to handle issues involving employer-employee relations and the resolution of commercial disputes.
An industrial employer and a union, a union member, or a union representative may engage in industrial arbitration to settle labor disputes and avoid the need for court action. Industrial arbitration is a sort of arbitration that aims to discover less expensive alternatives to going to court.
Management and labor are frequently eager to discuss and argue their claims with a third party because going to court or having negotiations fail can be hazardous for both parties. Industrial arbitration is the procedure through which labor and management will meet and attempt to resolve a disagreement.
This procedure frequently benefits both parties: the employee because it gives them greater bargaining power and prevents mass layoffs in a dispute, and the company because it lessens the likelihood of a strike or legal action. Nevertheless, the government has occasionally been known to intervene notwithstanding arbitration clauses and impose its remedies.
The IAC’s functions include the registration and certification of collective agreements, resolution of industrial disputes through the making of Court awards or Referee decisions, the interpretation and enforcement of awards, setting aside or variation of awards or collective agreements, mediation, and providing advisory services on matters of industrial relations.
Discuss the win-win approach to conflict resolution
When a disagreement arises within a company, a faulty characterization of the issue is frequently to blame. The importance of asking, “What is the problem we are trying to solve?” cannot be overstated. Remembering the example of the run-down middle school, compare the following inquiries and responses. Then pause to consider how remarkably different the solutions are although the problem is still present.
This strategy is employed for both dispute resolution and collective decision-making. It can be used in both professional and domestic settings.
Everyone concerned acknowledges the possibility of a win-win resolution to a dispute. There won’t be any motivation to move forward if there is no belief that such a resolution may be fulfilled.
Everyone agrees that this is the way they want to settle their dispute. It takes time, perseverance, and effort to find a win-win solution. They are only willing to use a win-win strategy to resolve the problem when the connection is significant to all parties.
Let’s take a look at the steps in the win-win approach to conflict resolution.
- The problem must be clearly stated first and foremost.
- Analyzing the issue carefully is the second step in creating a win-win solution to the substantive disagreement. Without the foundation of trust and cooperation, this analysis will not be successful.
- The third phase entails keeping an open mind while evaluating potential solutions. All parties involved must be prepared to accept the truth once the issue has been handled.
- Talk about how each person’s interests in the outcome.
- Each individual ascertains their actual demands. A win-win solution must satisfy all needs because they are fundamental requirements that cannot be changed.
- Each person chooses what they desire. The elements of wants are negotiable, and a solution will try to satisfy as many of them as feasible.
- Each person chooses what they desire. The elements of wants are negotiable, and a solution will try to satisfy as many of them as feasible.
- Everyone chooses their deal-breakers (what they absolutely will not or cannot do). There must not be a non-starter in the answer.
- Each individual decides how flexible they can be and what they are willing to offer to the solution.
- Everybody’s requirements wants, and deal-breakers are compiled and listed. This then serves as the standard for choosing a remedy.
- Everyone pools their creative talents to come up with potential answers.
- Then, each response is assessed in light of the requirements (needs, wants, and deal-breakers).
- Choose a solution that satisfies every requirement and as many desires as you can without being a deal-breaker.
- Every action that is required is decided upon by everyone, and those activities are planned.
What Is the Nature Of Contract In Business Law?
A contract is an agreement between two or more parties that establishes, clarifies, and regulates the parties’ respective rights and obligations. This agreement is legal and enforceable by law.
A contract can also be defined as a promise enforceable by law. The promise may be to do something or to refrain from doing something. The making of a contract requires the mutual assent of two or more persons, one of them ordinarily making an offer and another accepting.
The nature of contracts is that it is the jurisdiction that determines the circumstances under which promises made by the parties to the contract are legally binding. It does not specify the obligations and responsibilities that the law enforces but consists of a set of limiting principles. Parties can make their rights and obligations uploaded by law.
Nature of contract, which is essentially a contract, is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more persons that acquires the right to act on the one hand or refrain from acting on the other. Offers and acceptances are required to enter into a contract leading to a contract. And the law binds promises arising from offers and acceptances.
The scope of the contract defines all aspects of the document. Contracts have different forms, and the amount involved ranges from small to large amounts. Some contracts last for years while others have shorter deadlines. The materials found in contracts also vary depending on their purpose.
Process of contract
Offer or proposal: A contract must begin with an offer or a proposal from one party to the other. An offer is defined as a promise that is dependent on a certain act, promise, or forbearance given in exchange for the initial promise.
Acceptance: When an offer is made, the second party must accept or reject it. An acceptance is simply the assent of the other contracting party or parties to the terms stipulated in the contract.
Agreement: To form a legally enforceable contract, the parties must reach mutual assent. This is typically reached through an offer and an acceptance that does not vary the offer’s terms, which is known as the “mirror image rule”.
Legally binding: An agreement to become a contract must give rise to the legal obligations which mean duly enforceability by law.
Contracts may be bilateral or unilateral. A bilateral contract is an agreement in which each of the parties to the contract makes a promise or set of promises to each other. Unilateral contacts are less common. It is a case in which one party makes a promise, but the other side does not promise anything. In these cases, those accepting the offer are not required to communicate their acceptance to the offeror.
Essential elements of a contract
Agreement: The primary element that creates a contract between parties is an agreement, which is a result of offer and acceptance.
Free Consent: Consent of the parties is another important aspect of a contract. This means that the parties entering into the contract must agree upon the same thing in the same sense.
Competency: Competency refers to the capacity of the parties to enter into the contract. It means that they:
- have reached the age of maturity
- must be of sound mind,
- are not disqualified by law from contracting, etc.
Consideration: This is the agreed remuneration for the execution of the contract. It implies the price agreed to be paid for the promisor’s obligation by the promisee. It must be adequate and lawful.
Lawful object: The object for which the contract is created must be lawful, or else it is declared void.
Not expressly declared as void: The law should not expressly declare the contract as voids, such as a contract in restraint of marriage, trade, or legal proceedings.
Conclusion
The major objective of staffing is to fill the various positions within a company with qualified candidates. In this article, we looked at the staffing process and authority in management. It’s your turn to respond. Please, kindly use the comment box to ask your questions and make your suggestions.